Behind every extensive website there is a large treasure trove of know-how. At SISTRIX we always have the goal of sharing first-hand SEO-insider-knowledge. Four UK SEO experts with extensive experience in working on large websites will exclusively share their insights with you.
- Which skills does an SEO have to posses in order to work with extensive websites?
- Does it make sense to work with agencies or external consultants for these projects?
- SEO in large organizations – who needs to know what?
- How will SEO for extensive websites look in the future?
- Which strategies should I implement when it comes to the crawling and indexing of large websites?
- What advantages can I get from consciously deindexing a large amount of pages?
- How do I deal with steering and monitoring Googlebot on extensive websites?
- What strategies can I use in order to add internal links to millions of pages?
- Which obstacles often show up during the technical implementations?
- How do brand-searches from strong brands influence my keyword research?
- How can I organise the appropriation of my keyword material in a way that the different formats do not cannibalize each other?
- How can I discover and expand evergreen-content and how can I scale this process?
- What can I learn from my internal search?
- How does A/B-Testing help me?
- Which prerequisites does a extensive website have to put in place in order to make an internationalization through hreflang a possibility?
- How do I keep an overview over extensive projects and when does it make sense to break an evaluation down and look at individual keywords?
When it comes to SEO for extensive websites, Kirsty Hulse, Patrick Langridge, Alex Moss and Stephen Kenwright can draw from their extensive experience of working with large projects and know-how to implement the necessary processes in or for large organizations.
Which skills does an SEO have to posses in order to work with extensive websites?
Large and extensive websites have their very own kind of requirements. In order to implement good SEO for large websites, a company needs a team of technical and editorial staff and, on top of that, it is very helpful to have a project manager who ensures the communication between everyone involved.
Set up meetings at the start of large projects for everyone involved and get in touch with other departments who also work on the same project.
With extensive websites it can be useful to have teams that are specialist in different fields.
Make friends with specific people as an SEO, for example with the developers, to have the technical side on board with you. You need to have a thorough understanding of what your companies’ goals are. Last but not least: Understand your client and use the language he understands and the words and topics that are relevant to them.
Does it make sense to work with agencies or external consultants for these projects?
Usually companies will not have inhouse specialists for every topic. Big companies must rely on external resources for campaigns or times when it gets busy. If your company does not need a ressource all the time, it makes sense to get an external consultants on board when necessary.
Finding a good consultants or freelancers can be problematic. But even at a higher cost, they might be more cost-effective over time, by conserving precious resources on your team.
Skillsets become more and more niche and SEO work becomes more specialised – getting an SEO consultant can be helpful.
When you are hiring a consultant for a short term project and still retain an agency, long-term, it may become a challenge to balance their goals. Make sure that the long-term goals of your organization are always front and center.
SEO in large organizations – who needs to know what?
SEO is not a self-sustained project within a company. When it comes to SEO, there are always other people within the company who are involved either directly or indirectly. Speak to as many people as possible who are involved in the project to understand their KPIs and perspectives. This way you can explain to them your reasoning if they have specific questions. Arrange meetings with all stakeholders early on and also speak with them in 1 on 1 meetings. Listen to what they want: Build relationships over time with different departments (PR, DEV). Make sure to gain their trust and try to help them achieve their goals.
SEOs should spend more time listening to other departments, instead of talking at them.
How will SEO for extensive websites look in the future?
SEO as an industry is constantly changing. In the future, we can expect that “getting things done” will get harder. You already have to know a wide array of technical topics that border on SEO and, in the future, this will only increase.
It is not unlikely that, today, we might only be doing half of the things we might be required to do in five years from now.
Educate clients and teach their developers and editorial staff how to incorporate SEO into their processes. It may very well get to the point where SEOs do not execute SEO anymore but rather teach specialists how to consider search, in order to retain value.
SEO for large projects is a large and complex field, but the question is how do leading SEO-experts deal with technical problems when it comes to extensive SEO?
Let’s just ask them ourselves! We consulted top SEOs from the UK, Germany and Spain and asked them specific questions on this topic.

Aside from our UK guests, Kirsty Hulse, Alex Moss, Patrick Langridge and Stephen Kenwright, we have Benedikt Kirch, Dominik Schwarz, Nedim Šabić, Markus Hövener and Daniel Reeh for Germany as well as Carlos Redondo, Pedro Martinez, Lakil Essady und Daniel Pinillos for Spain.
Which strategies should I implement when it comes to the crawling and indexing of large websites?
When it comes to the technical implementation of crawling and indexing, our experts agree that strategic considerations about which pages you really need are one of the strongest levers you can use.

meinestadt.de
Website content: as much as needed, as little as possible.
One recurring problem, when it comes to crawling and indexing, is duplicate content that is created through filters and other parameters. In these situations it is helpful to transfer as many parameters as possible from the URL into cookies, which can then be blocked for Google. When it comes to filters and facetted navigations, you can use the PRG-Pattern to keep Google from crawling and indexing them.
Additionally, it is a good idea to keep an eye on the click levels that Googlebot has to go through on your site, in order to get to a specific piece of content. The deeper a page is hidden in the navigation or the internal linkgraph, the harder it becomes for Googlebot to find it, in any reasonable amount of time.
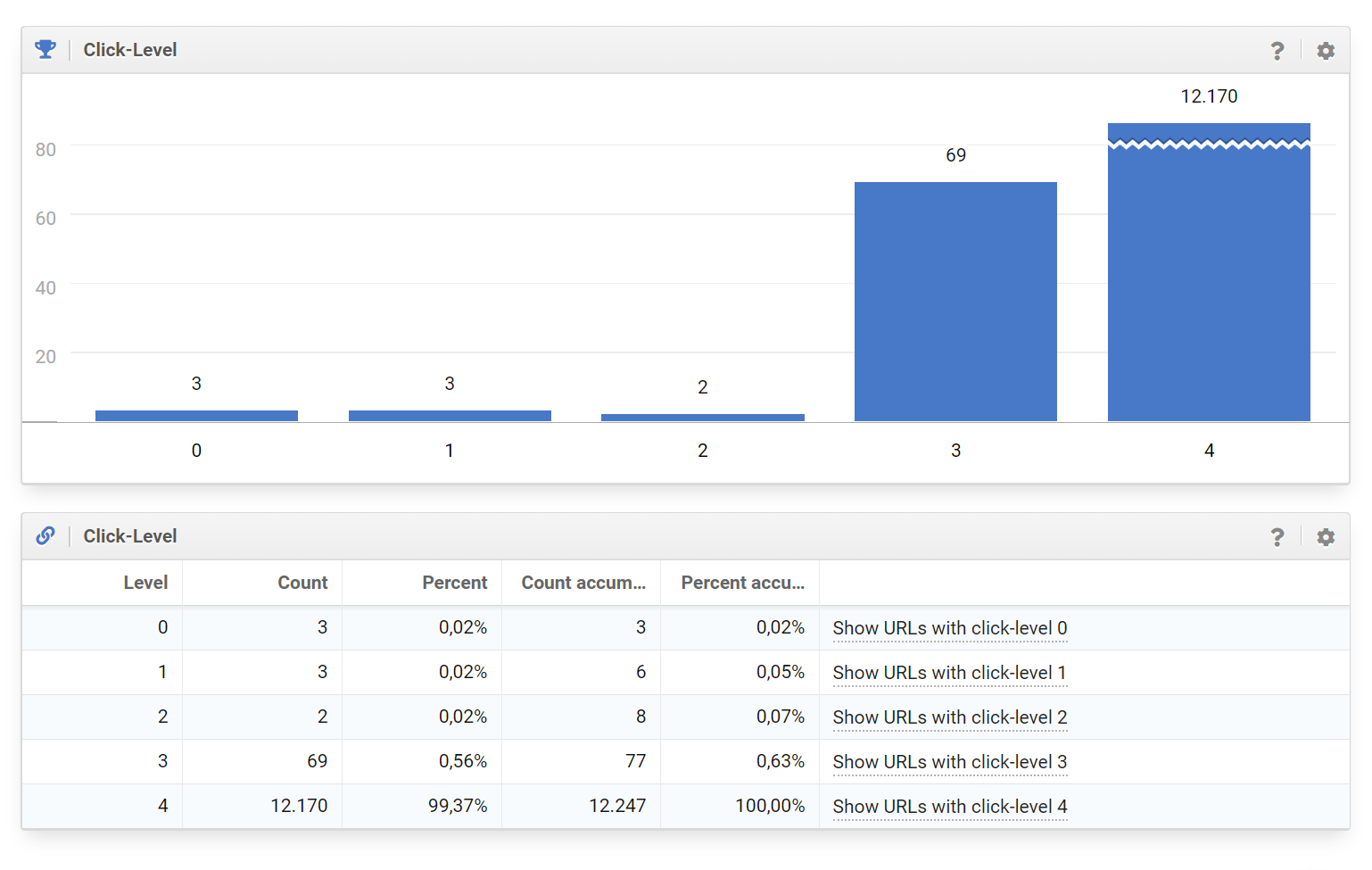
A method that proved very useful for extensive websites are topic-clusters. Due to the fact that, with large websites, you do not have the ability anymore to look at and evaluate each individual page, it becomes especially important to have a methodical approach to linking within your clusters.
Using XML-, picture-, video- and product-sitemaps can help Googlebot better understand extensive websites. Have an algorithmic process of creating these files and do not create them by hand for large and extensive websites.
Another way you can approach crawling is by improving the pagespeed of your pages. This way, Googlebot will be able to see more pages in the same time and with the same resources it used before.
All in all, everyone agreed that there is no one-size-fits-all solution for extensive websites. Once your site gets to a certain size it becomes absolutely necessary that you understand all your systems and have full control over them.
What advantages can I get from consciously deindexing a large amount of pages?
Deindexing a large amount of pages for a domain can have quite the positive effect on the website. Our experts recommend to create a well thought out strategy beforehand.
Once you start questioning whether specific pages or even whole parts of your website might have no business being in the index you are metaphorically at the point where you are trying to shut the stable door after the horse has bolted. Editorial articles and content, for example, might be ripe for an update instead of a being deindexed.

hometogo.de
You should decide between “deindexing” and “not creating in the first place.
Deindexing a large amount of pages for a domain can have quite the positive effect on the website. Our experts recommend to create a well thought out strategy beforehand.
Once you start questioning whether specific pages or even whole parts of your website might have no business being in the index you are metaphorically at the point where you are trying to shut the stable door after the horse has bolted. Editorial articles and content, for example, might be ripe for an update instead of a being deindexed.
Getting rid of large, unnecessary parts of a website can lead to an improvement of the average signals for the rest of the site. Best case scenario, your large scale deindexing measure will only leave behind pages that are an essential part of your site and of above-than-average quality.
If hyperdynamic content from your website managed to find a way into the index, you can confidently deindex it. The same goes for parameters and paginations. Both of these need to be handled in a clean technical way by your system. Please also keep in mind that the “noindex” attribute will only affect indexing, not the crawling of your site.
Using Google-hacks, such as implementing both “noindex” and “follow” on pagination pages, for example, can be an effective band-aid for a while. Problems can arise though if Google decides to change how their crawl and process these signals.
Getting rid of a large number of pages can also have a positive effect on your navigation and internal linking strategy, by simplifying both, which can then also help Googlebot crawl your resources more thoroughly and find more of the pages you really want Google to see.
How do I deal with steering and monitoring Googlebot on extensive websites?
Once your website can be considered large and extensive, steering and monitoring Googlebot will gain in significance.
You can get a first important glance into Googlebots crawling behaviour through the “crawling-statistics” report in the Google Search Console. It will give you information on how many pages of the domain have been crawled per day. If, for example, you have 1.000.000 URLs on your domain and Google crawls a mere 20.000 pages a day, then it is quite possible that it will be a long time until each of your pages has been seen anew by Googlebot.

screamingfrog.co.uk
If you have the right kind of information-architecture it is a much cleaner way of directing Google than the robots file. Set up a logical path through your site, which makes sense for both users and searchengines.
With an extensive website it is advisable to analyse your own server logfiles, as they will give you much more up-to-date information as compared to the Search Console. It is also very useful to set up alerts for specific metrics, so that you can quickly get a notice if there are deviations from the norm. Automatic processes are a must as you will not be able to deal with these logfiles by hand.
If you do not yet have a system in place for your analyses, it may be a good idea to start with an ELK-stack. This is a combination between Elastic Search, Logstash and Kibana, which can help you to collect, save and evaluate your log-files.

crawlo.com
Not everything in your logs will be truthful. This means you have to specifically check and distinguish between the true Googlebot and fakes.
You can also use an external crawler to run through your site and simulate Googlebot. This can quickly make you aware of problems where Google may get stuck or have problems navigating your site.
What strategies can I use in order to add internal links to millions of pages?
With a growing number of individual pages, it becomes more and more important that all of them are linked to internally, as this will help users and Googlebot navigate through the website. And while there is no blanket solution available to automatically provide hundreds of thousands and even millions of pages with internal links, you do need an automated solution.
Generally, it makes a lot of sense to consider whether your content is segmented in a way where you can work with silos or if you want to have a very broad navigation, in which case it becomes feasible to work with mega-menus.
Both of these implementations will put you in a position where you can automatically supply a large amount of pages with internal links. When it comes to deciding which method you want to use it is important to have clear strategic goals of what you want to achieve with each method and with your navigation, in general.

branded3.com
An obvious point here is having breadcrumb-navigation, as well as using headers and footers.
When it comes down to deciding which pages should be linked to internally the most, you can use your Analytics data to find the page types with the most traffic, such as category pages.
Two additional, helpful strategies are using internal links similar to how Wikipedia does, as well as to set up an automated system that will add links to similar and related pages, for example, as part of an article’s sidebar.
Which obstacles often show up during the technical implementations?
Being able to implement your entire packet of measures is quite the challenge for a website of any size. Once you step into large and extensive websites this becomes even more true. For this reason we asked our experts to share typical obstacles which they have encountered over and over again, when it comes to the technical implementations of SEO measures.
One of the most common obstacles is a missing technical capacity to implement the changes, at all. If you did not manage to secure the necessary budget and resources from your IT department or external contractor, you will quickly have the problem that your well laid plans are not implemented in full, or, worst-case, not at all.

obi.de
Have a plan for each of you page types, which SEO measure should work how. This makes life easier for your IT as well as yourself, in that you can quickly get an overview over the measures that have already been implemented.
Two classics in the field of technical obstacles are missing or wrong tags. Be it the hreflang markup or the unambiguous setup of a canonical version of a page.
Interestingly, the one measure that is underrated the most is communication. Behind large websites you will often have large organisations with a large number of stakeholders in the production process. This may sadly mean that the saying, “too many cooks spoil the broth” can become a reality.
Investing into the communication process between stakeholders is very worth your resources if information manages to flow more freely afterwards. You can only find out what it is that others don’t know by talking to each other. Your goal should always be the creation of an understanding for why specific changes are planned.
At the same time, it is important to set up automated processes, such as unit-tests, in order to make sure that, before each release, everything is working as expected. If you are working in an Agile development process, setting up SEO-Checkpoints has proven to be a very effective method of getting ahead of possible errors.
How do brand-searches from strong brands influence my keyword research?
Often large websites will belong to well known brands. The brand-searches that this encompasses can give you insightful information on your website.
While our experts agree that having a strong brand will not influence your regular keyword research, they do add that evaluating the brand-searches can be quite useful.
Through the brand-search you can gain insights into which parts of your website are seen as brand-specific by your users. Large organisations and brands also have the ability to use other channels, such as TV-Ads for example, to create searchvolume for newly created keywords. If you can create your own keywords the market environment for this keyword will also be worlds apart than that of generic search queries.

firecask.com
It depends on how positive the brand recognition is by the public. It if is not the best, your keyword research will also have to encompass reputation management issues.
How can I organise the appropriation of my keyword material in a way that the different formats do not cannibalize each other?
If you work for a large website you will often have a large pool of content you can draw from for different content formats, such as blog, video, guides. With these possibilities also comes the central question of how you can allocate content to these different formats without them cannibalizing each other.
The most useful help you will find is user intent. If you take a look at Google’s search results for a specific query, you will see the content formats that users are currently preferring. You can scale this approach by evaluating the SERP-Snippets for the keywords you want to monitor. This will give you the ability to see which SERP integrations are part of specific searches and even clusters.
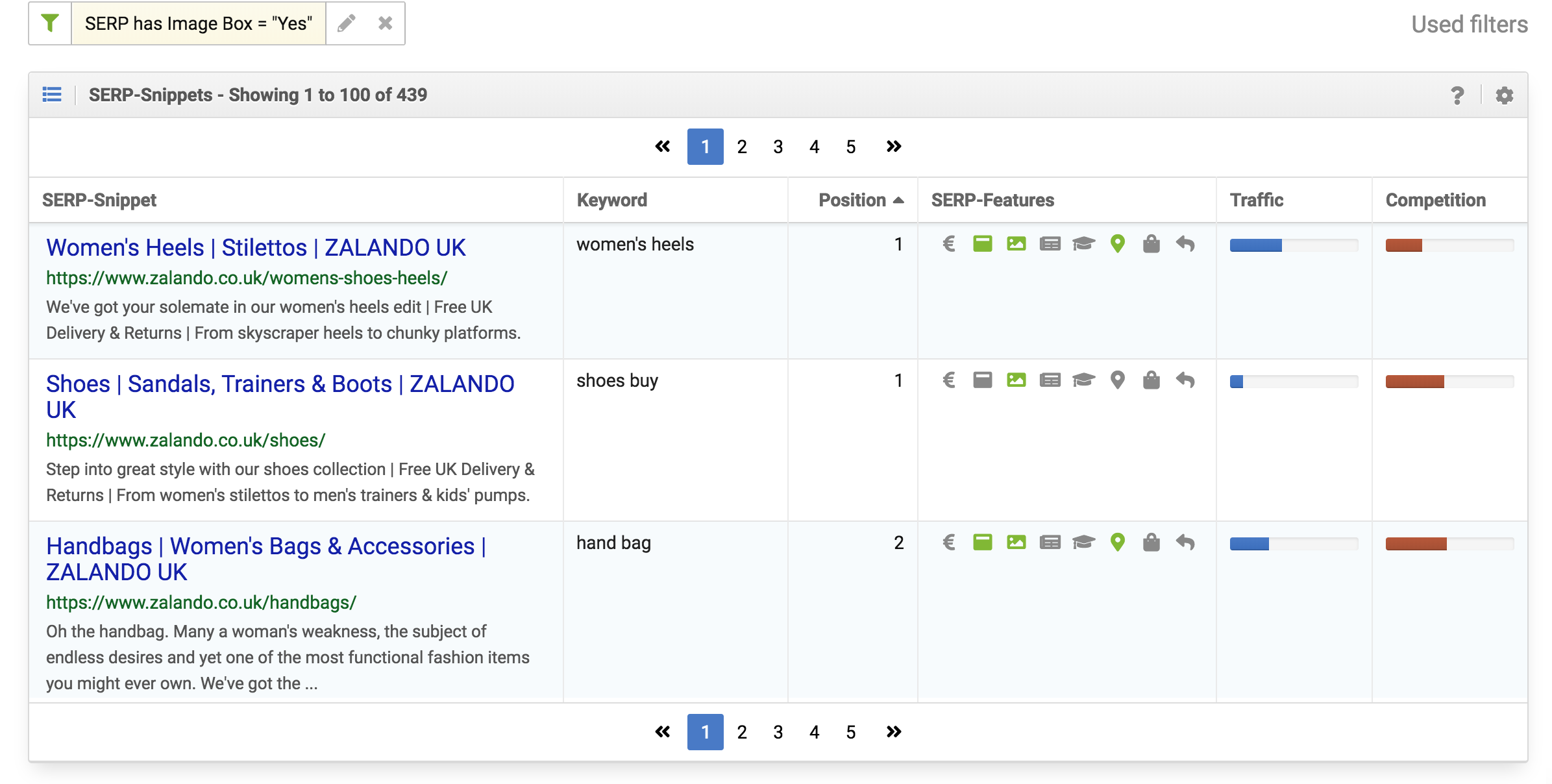
In order to unveil keyword cannibalization you will need tools that can show you which keywords have multiple pages ranking or where different pages take the place of each other within a short time. For these results you will need to set up a process of editorial decisions where only one of the pages is chosen to be the best representation for that keyword.
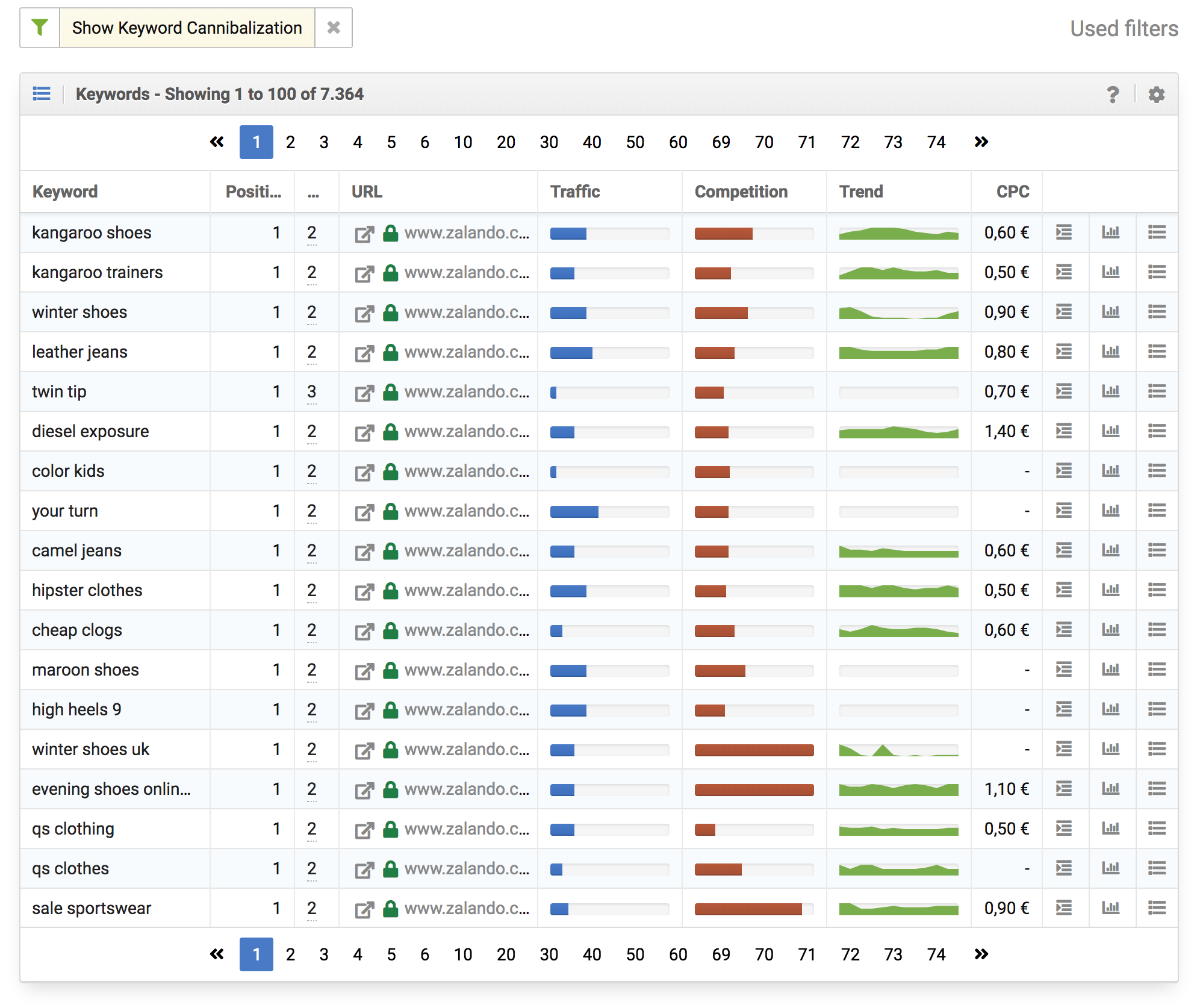

safecont.com
In order to preven cannibalization, we sort our content from general to specific. If two results show up within one search, we will always prefer the general result.
An important step on the road to preventing cannibalization is a strict and logical structure within the information architecture of the website. Through it, there should be a clear process of when new pages should be created, which ones should be created and where within the structure of the site they should be located? It is important to prevent the haphazard creation of similar pieces of content by different teams, that are then strewn randomly across your plattform.
How can I discover and expand evergreen-content and how can I scale this process?
The Internet has many advantages. On of them is the possibility for a piece of content to stand the test of time and satisfy visitors for years and years. Unlike daily- or weekly newspapers, you do not have to constantly create similar pieces of content just to fill up the paper.
These pieces of evergreen content have proven to be strong traffic- and trust-purveyors for a website, time and time again. This makes them so important and is also the reason why you should invest in finding your evergreen content and expanding on it.
You can use your web analytics tool to identify evergreen content, by segmenting by topic clusters that manage to continuously, or seasonally, attract high traffic streams over numerous years. Additionally you can check for URLs that rank for numerous keywords within the Top-10 results.
Luckily, you are not limited to your own website when looking for useful content. Run a content-gap-analysis against your competiton and discover which content of theirs is evergreen.
When you create content that is supposed to last the test of time, it is extremely helpful to have a distinct process, which already checks a page during the conceptual phase for whether it has what it takes to become evergreen content. In order to expand your evergreen content it helps to work with topic-clusters through which you can identify new articles.
One thing to keep in mind is that, regardless of whether we talk about creating or expanding content, this will always include an editorial process which cannot be outsourced to a piece of software. You can also scale this process well, but only with an increase in the size of your editorial team.

Freiberuflicher SEO-Berater
You can only scale this by human hand if you want to add actual value to your users!
If you do not yet have an editorial process for creating or expanding evergreen formats, it is a good time to set one up or integrate into an existing process. This process should have clear rules for when and where an article needs to be adapted or updated and which form it should be in.
What can I learn from my internal search?
If you have an extensive website you need an internal search. There is a wide range of systems available, from out-of-the-box solutions to individual creations, all with varying degrees of quality. There is a number of good reasons for why the internal search is such a valuable tool – especially for your users.
Your Internal search is there mostly for the visitors of your page, who might not have found what they were looking for or did not want to use your navigation. At the same time, it is also your visitors who are used to search working well and giving them suitable results, which sets the bar quite high.
This alone should be reason enough to invest in your website’s internal search. Problems usually arise from not having someone in charge of search. Have a dedicated search architect or team in your company, whose job it is to make your internal search work.

manyminds.digital
On very large websites, the internal search can also take over an important navigational role, for all visitors who do not wish to click through your category pages.
You can use the information you get from your internal search and share it with divisions across your company, which can help them make better decisions. You can, for example, use your internal search data to identify pages which are highly frequented, but hard to find in your navigation. Additionally, you can figure out what your visitors expect from your website.
Especially interesting: If you take a look at an evaluation of all search results from your internal search, which searches returned no results, you get a good idea of which search queries there are, that you are missing the searchers intent.
From a technological standpoint, it is important to keep your websites search results out of Google’s search result pages, as Google really does not like search results in search results (SERPs-in-SERPs).
How does A/B-Testing help me?
Setting up tests to validate or falsify your own hypotheses has proven to be a very useful tool in the conversion optimisation, where you do not have to rely on your gut feeling to make decisions, but can use data to answer your questions.
When we talk about A/B-tests, we have to differentiate between tests to check user interactions (conversion optimization) and A/B-tests to figure out SEO-ranking-factors. Tests of ranking factors are very hard to set up, as many of the factors Google uses cannot be controlled for. Tests for the user interactions, on the other hand, are a godsend and should be used as often as possible.

Unidad Editorial
If you do not test how Google reacts to changes on your own page, you will never understand their process. Do not be afraid of log-analyses or A/B-tests. Testing is the only way you can get better
When it comes to implementing tests, you can choose from a large number of external service providers or set up an internal team of specialists. Whichever way you decide, it is extremely important to have a consistent person of contact who is available throughout the entire test. Something that may often become problematic are deployments before the weekend and holidays. If during this time a problem occurs, there is often no one there to fix it, in any reasonable amount of time.
Something else to consider is that most providers use testing frameworks build on JavaScript. This gives those A/B-tests the theoretical ability to alter your entire page, or make it unusable. This makes it imperative to set up a constant monitoring which will alert you if a specific change has jumbled your website.
It may also prove useful to have an emergency break, which will stop the test and get rid of the code without your IT or external service provider having to lift a finger.
In order to prevent duplicate content problems, you should always use the current (real) version of the page, A, as the canonical URL. Additionally, you can make sure that search engines will always be send this version of the page, by filtering their user-agent strings.
Which prerequisites does a extensive website have to put in place in order to make an internationalization through hreflang a possibility?
Through the hreflang markup, Google has created a way to connect different language versions of the same page, so that a search engine can understand their relationship. And while hreflang is based on a small set of simple rules, there is still a lot that can go wrong, which may often cause Google to ignore the entire construct.
When you plan on using hreflang markup for your website, it is essential to take a close look at Google’s prerequisites for using the hreflang markup. Aside from numerous technical potholes conceptional mistakes come in as a close second.
The best setup you may have or could create is an internal system which saves how all individual pages throughout your languages belong together This includes not only URLs but also article numbers and the like, especially if they differ between languages and countries.

bloofusion.de
The basic requirement for a propper use of hreflang-tags is having an identical website structure throughout your country pages.
There are quite a lot of ways of how you can patch-up and band-aid a site in order to „make hreflang work“. But it is only through a clean, technical implementation that you can quickly and easily implement new pages or even language versions into your site, without also adding a huge extra implementation workload for your team.
How do I keep an overview over extensive projects and when does it make sense to break an evaluation down and look at individual keywords?
Once you get past a few tens of thousands of pages, it is not practical anymore to evaluate individual pages. If you have hundred thousands or millions of pages, this is true even more so.
When working with extensive websites, it is helpful to set up automatic alerts through your internal analysis tools. These should send you a notice if any metric sways too far from the norm. This does not mean you have to panic at every notice, though. It is extremely helpful to notice trends very early.

FunnelPunk.com
In order to have an efficient overview over large projects, it is advisable to monitor entire keyword groups – for each landing page, top- and product-pages.
These trends, whether they are good or bad, should then be analysed more closely. You will want to know what caused the trend and, for negative trends, fix whatever is wrong or, for positive trends, do more of what is working.
For you overall evaluation you can use indices, especially when it comes to noticing possible Google Updates, which you can evaluate over a large mass of examples. Additionally, it is a good idea to set up a keyword monitoring for your own keyword set, which you can then use to get a better view of specific topics or niches.