Every now and then we come across easily-avoided SEO mistakes that creep in, especially among SEO beginners. That’s reason enough for us to analyse these common SEO beginner errors and for us to provide an answer.
The Importance of SEO is underestimated
The most important thing first: your own attitude to SEO. Search engine optimisation is not a one-time project, but a long-term process. SEO is permanent work and only successful if it is continuously practised. Search engines are the most widely used application on the Internet and therefore SEO should get the resources of time, personnel and budget in your business that it deserves.
Personalised search results
Webmasters get a distorted image when they search their own website on Google because the search engine provides users with personalised search results. Therefore, websites that are frequently clicked by the logged-in user automatically receive better rankings. The result: The search results for your own websites usually look better than they actually are.
To get around this, you can easily disable personalised search results.
This ensures that the rankings displayed to you are as neutral as possible and are not influenced by your personal click and surfing behaviour.
Keywords Meta-Tag
Google has never used the keywords meta-tag for rankings in the search results.
Google doesn’t use the keywords meta tag in web search
Matt Cutts
Use your energy on more important SEO topics: for example, on the actual Google ranking factors. Which are these? We discussed many key Google ranking factors with the most well-known SEO experts in Germany. Or, take a look at meta tags that are really SEO-relevant.
No redirects
If your site is accessible across multiple domains or you want to avoid duplicate content, be sure to use 301 redirects. Decide on a domain and forward all others by using the 301 redirect (permanent forwarding).
Without proper redirects, Google may not know which of your domains should rank in search results. That may look like this:
But that’s not all! Your trusted signals (backlinks, for example) which you have laboriously built up, are spread over multiple domains and, understandably, only develop a fraction of their actual performance.

Incidentally, this also applies to host names, transfer protocols or session IDs. URLs should always be unique.
No control over your CMS or shop system
Even though most providers of CMS and shop systems advertise offering “search engine friendly” applications, in practice, many still have to be adapted to the individual application of the webmaster. Typical problems in this context are (internal) duplicate content, dynamic URLs, the inability to free internal links or the fact that titles, headings and meta-descriptions can not be maintained individually for each page.
Gain control
For established CMS and shop systems, there are useful SEO extensions (plug-ins, extensions or add-ons). Further adjustments may require deeper programming skills. It makes sense to check the limits and possibilities of the CMS solutions in advance. Make sure that the technical basics for your search engine optimisation are given or can still be created.
Not enough good content
Do not create your content for a search engine. Place your readers at the centre of your efforts and earn valuable user feedback with valuable content. Google evaluates, among other things, the user behaviour and external links as signals for good content – and these signals come (or don’t come!) from your readers.
Good content is one of the most important ranking factors. If you want to know more about good content, here’s some additional information for you:
- Ranking Factors – Content Quality.
- User first: Why many company websites are not successful with Google.
- Holistic Content – Hype or SEO Magic Bullet.
Poor external linking
That links are very important for a good ranking is beyond question. But how good your links are for your website depends on, among other things
- Quality of the links
- Number of links
- Anchor text
- The mix of links
- Google rating of individual links
Keep your hands away from bad links.
Bad links (Quick & Dirty) are, for example, links from link-sharing programs, article directories, press portals, low-quality websites, and link sellers.
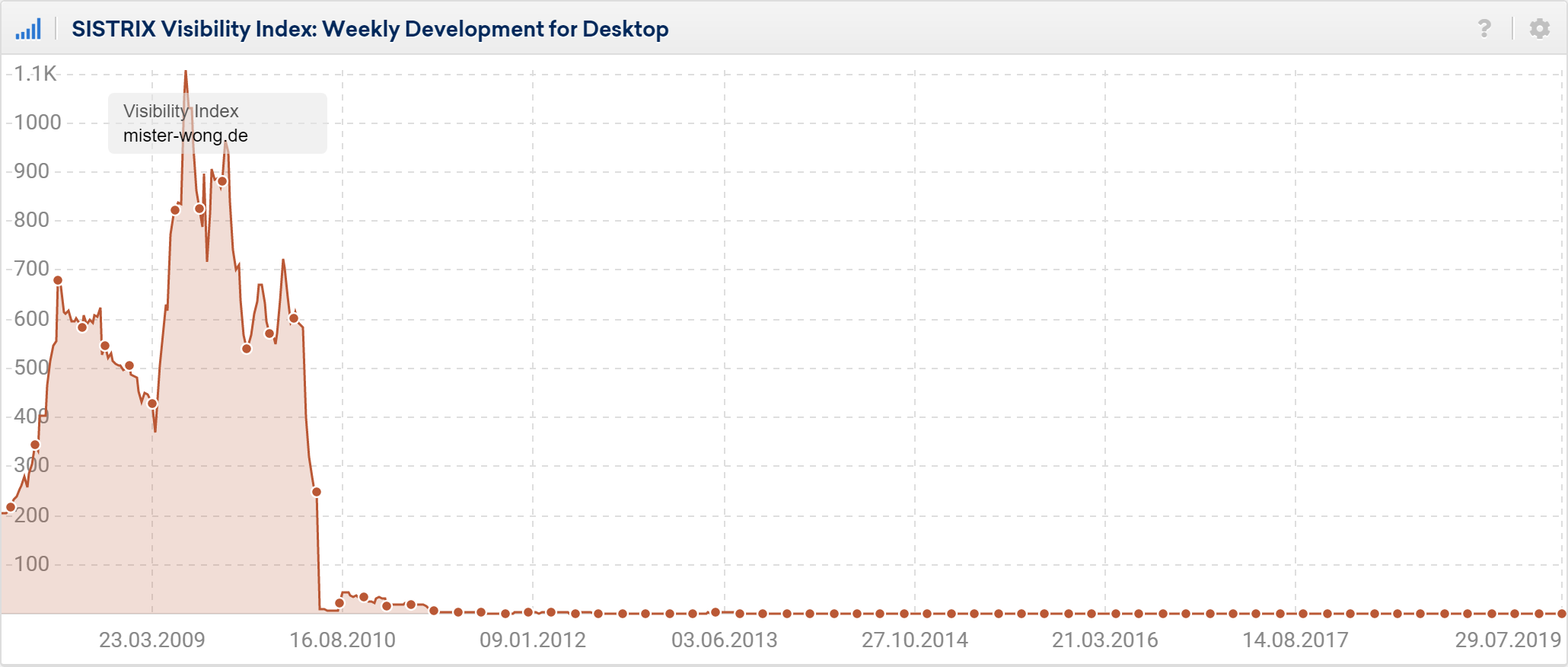
It’s important to keep an eye on your own links, because once trusted sites that link to your domain lose their rankings, Google probably will not trust the outbound links on this site – a prime example of this is the once-heavily-linked page in Germany and former social bookmarking platform: mister-wong.de.
Try to get good backlinks. Good links are those that are clicked, in the best case often, by users. It’s as simple as that!
The goal of any website operator should be to earn more links that comply with Google’s policies.
Bad internal linking and poor anchor texts
Often the link text (anchor text) is used incorrectly for internal links. Anchor text should always describe the specific content of the landing page as a keyword and be made up exactly of the keyword for which you want to rank.
Make sure that internal links are used intensively and consistently for the keywords that describe the content of the linked page and for which you want to rank. More about this can be found in our knowledge text: Internal link optimisation.