Search engines do not understand language or content the way in which users do. Therefore, when writing content for the web, we need to give search engines as many chances as possible to understand what it is we are saying. That way, they can ensure the results they give are as relevant as possible.
The main hurdle for search engines is that content is complex. After all, a film review website is very different from a yoga video tutorial website. With so many different search terms and content types, search engines can have a difficult time keeping up.
One such tactic to bring about clarity is to use structured data. Structured data is metadata that you can add to the code of the page to describe its content. The data is written in a way that specifically speaks to search engines.
What Is Structured Data Used For?
Structured data enhanced and tags key pieces of information that are specific to a particular category. This data can be use by a search engine to enhance results which can be far more engaging to users. The extra information helps the user decide if the result is relevant. This in turn helps to reduce the site’s bounce rate, because the decision about relevancy is made before the user even clicks on the page.
Is structured data good for SEO?
Helping search engines to crawl and understand content is one of the main SEO tasks and structured data is a tool that can help. Not only that, it may be the only way into some Google search results features that require structured data such as recipes, and other features such as job postings, video features and events that are show in the results for appropriate searches.
Structured Data Examples
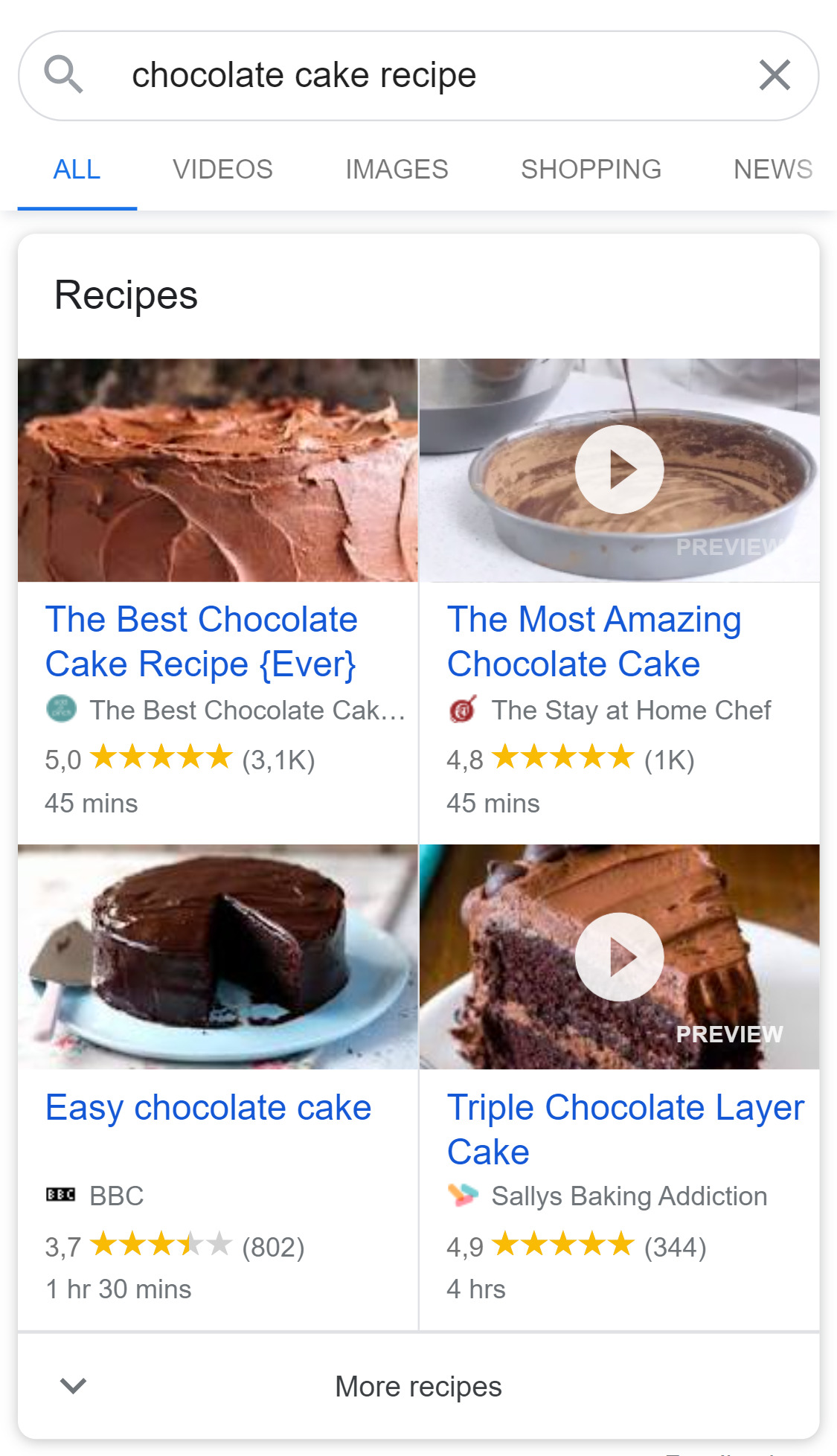
Have you ever noticed that sometimes a search result contains more than just the URL and meta description? For example, it could display images, videos or even product ratings alongside the result. This is no accident, especially as we are more likely to click on such a result compared with a bland text based search result.
It all comes down to the use of structured data on the website, which allows for what’s known as rich results to be generated on the search engine results page. Essentially, the website author has broken down the information in a way the search engine understands, so that it can translate this in a way the user will understand.
Using structured data, a search engine result for a recipe would contain the following information:
- Image of dish
- Recipe name
- Recipe URL location
- Recipe rating
- Recipe cook time
- Recipe ingredient list
The above might seem like a lot of information for the user to digest. However, search engines neatly display the information using a combination of image and text based descriptions, making it actually appear very engaging. Results are also displayed side by side instead of horizontally to ensure user friendliness.
Structured Data Schema
Search engines recognised the need to develop a language to break down content on the internet, in a way that could be read by their technology. That’s why Google, Bing, Yahoo and Yandex collectively came together to build Schema.org. The website allows you to find all of the structured data markups that are supported by these four search engines to use for your own content.
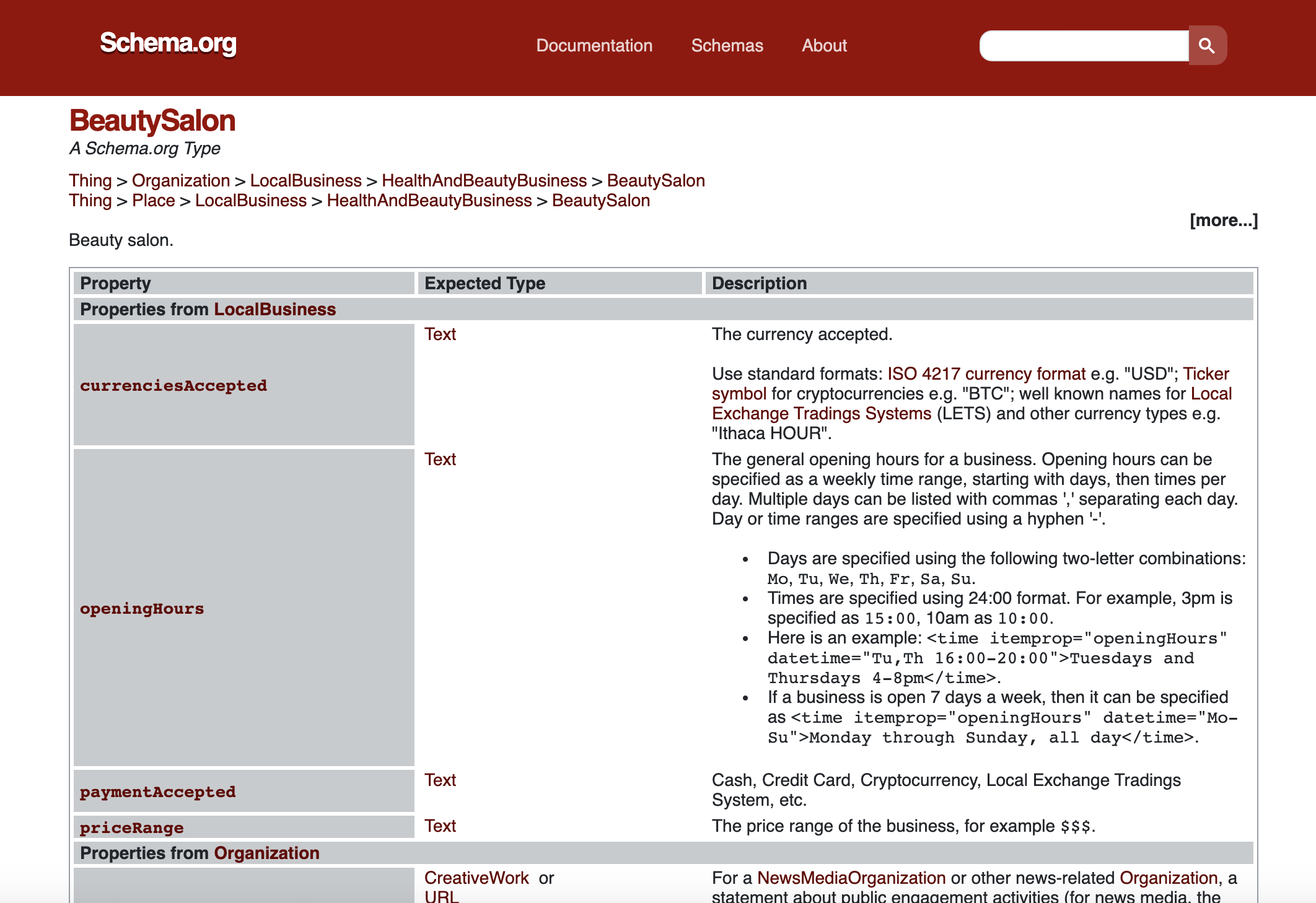
The idea is that you can find all of the related structured data for your niche, so that it can be generated as rich results on search engines.
Let’s say our business is a beauty salon. Schema makes it possible to show the currencies accepted, opening hours, payment accepted and price range of our salon. All of this information will be given to the customer on a search engine result, helping them to make a better purchase decision.
There are endless other structured data types that Schema can provide for practically any industry or product type. In terms of events, schema can provide tools to display upcoming shows and how much tickets cost. Or for books, it can allow you to display a picture of the cover, the ISBN number and so on.
We have more information available on what Schema markup is and how it can be used.
How Does Google Use Structured Data?
Search engines are constantly looking to improve their offering to users, and structured data is just one way they are getting ahead.
Type any search into Google, and you’ll usually find rich results generated by the use of structured data at the top. It’s no coincidence these results appear first because search engines want to immediately grab your attention, by providing everything you need without having to endlessly scroll.
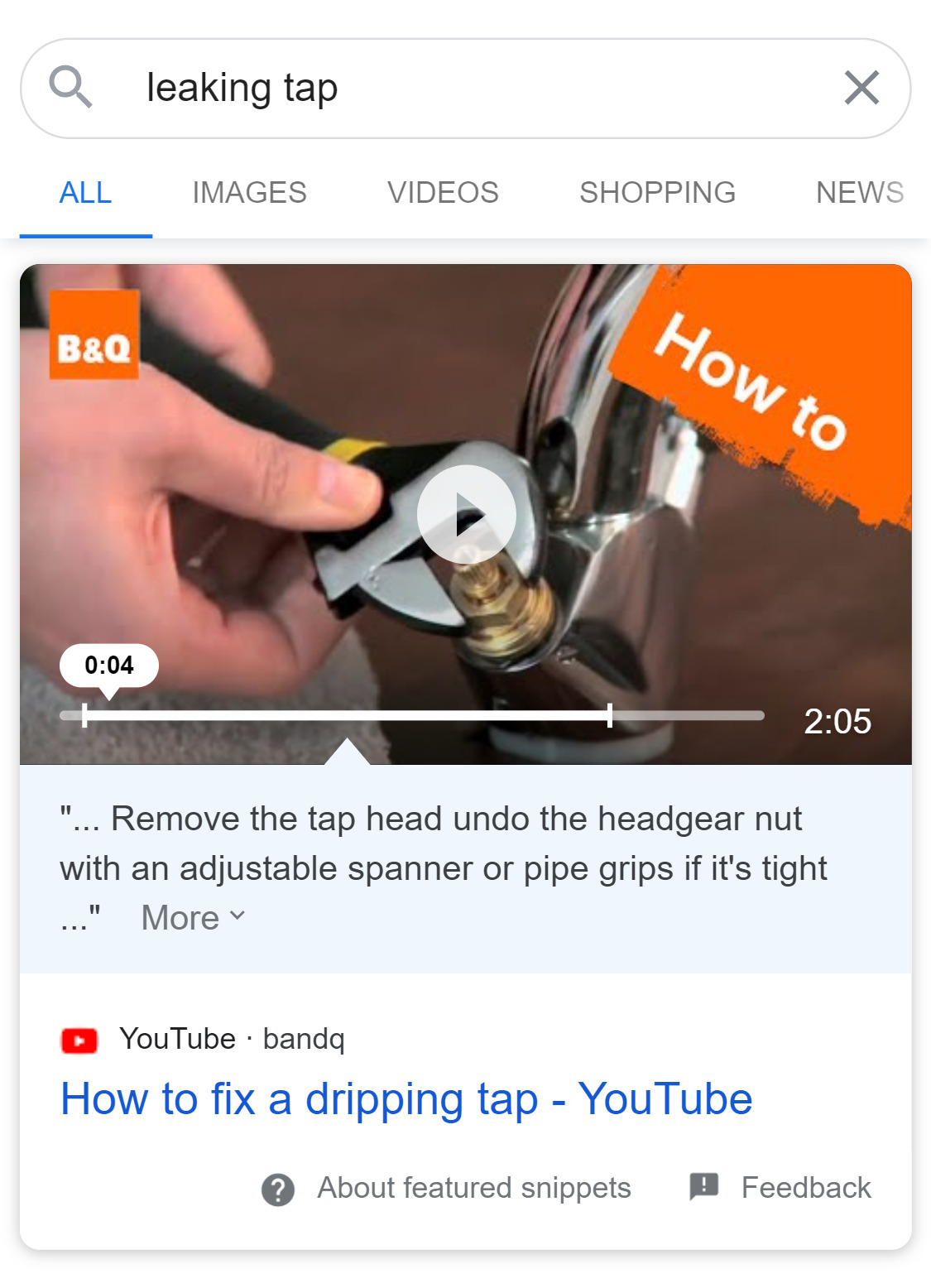
Say you Google the phrase ‘leaking tap’. The first result is a video tutorial on how to fix a leaking tap which can play in Google itself, meaning you don’t even have to leave their platform to get what you need. Underneath is more DIY videos before you get to the text based results.
What Is Structured Data For SEO?
If you’re familiar with SEO, you’ll know that it’s important to make your website as visible as possible on search results. Keywords are integral to SEO but are far from the only tactic you can employ.
Sometimes a brilliantly written H1 tag is not enough to get users to click on a result. After all, humans are both visual and inquisitive creatures. Structured data allows for both of these needs to be met by the way it will allow your search engine results to be displayed.
Structured data doesn’t just present your website at the top of a search result. It offers visual information and key points about the content. All of which is not only helpful but acts as a marketing tool in itself.
Otherwise, the user would have to manually scan the entire website for such information to decide if it was relevant. Schema helps cut out the middle man, all whilst creating more engaging results. The more times your rich results are clicked on, the higher up the rankings your page will go.
What Is Markup?
Markup is a piece of code that can be added into your HTML microdata and forms the basis of how structured data works. Using Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper, you can select the type of content you are looking to promote. The tool will allow you to add schema markup to your page.
The content could be a restaurant menu delivered in a text form, reviews of a game or the cost of a product. In essence, any information relating to the product or service can be entered using schema markup.
Markup can be tested using the Rich Results Testing Tool or the Structured data testing tool. We have written a guide to the testing tools.
What Is Unstructured Data
Approximately 80% of data can be classed as unstructured data. The term refers to anything that cannot be ‘structured’ into a tabular format. Examples of unstructured data would be text based posts, emails, social media posts, videos and voice notes.
Previously, it was difficult to analyse structured data because it had no real format you could arrange it in such as a spreadsheet. However, companies such as Facebook are now implementing deep learning technology.
This is helping to uncover what users react to, and how long they spend interacting with a piece of content. All of which is helping platforms make sense of unstructured data, by interpreting not only the content itself but the sentiment behind it.
Conclusion
When you are trying to get your business seen on search engines, it’s not enough to use basic tactics alone. Structured data is a more advanced technique that makes sure your content offers helpful insights that will make it more likely for a user to click on the result.
Rather than a generic URL and meta description, if you use structured data users will get a much more insightful result. Given the way of implementing structured data – schema – was developed by the search engine giants, it’s definitely worth tapping into if you want your content to be seen online.