Changing the domain name does not have to be the cause for any (long lasting) negative SEO effects. As long as you plan the move carefully and do it correctly, you do not have to fear ranking losses.
- Lily Ray talks about the important SEO tasks relating to a domain migration
- The change of address tool in the Google Search Console
- 301-redirects on the old domain
- Checking your internal links
- Have Google crawl the new domain
- Monitor your domain move
- 301 redirects do not have a high damping factor
- Video: Matt Cutts, Google on multiple 301 redirects
- Additional information about this topic:
Lily Ray talks about the important SEO tasks relating to a domain migration
In order to move your domain, you should tell Google that you changed the name or hostname / domain name of your website. You do so through the Google Search Console (GSC) and then you have to redirect all the content from the old domain to the new, with the help of 301-redirects.
The following steps and requirements are necessary in order to ensure the domain move goes through without a hitch:
- the domain you used so far has to be verified in the GSC
- the new domain also has to be verified in the GSC (using the same account)
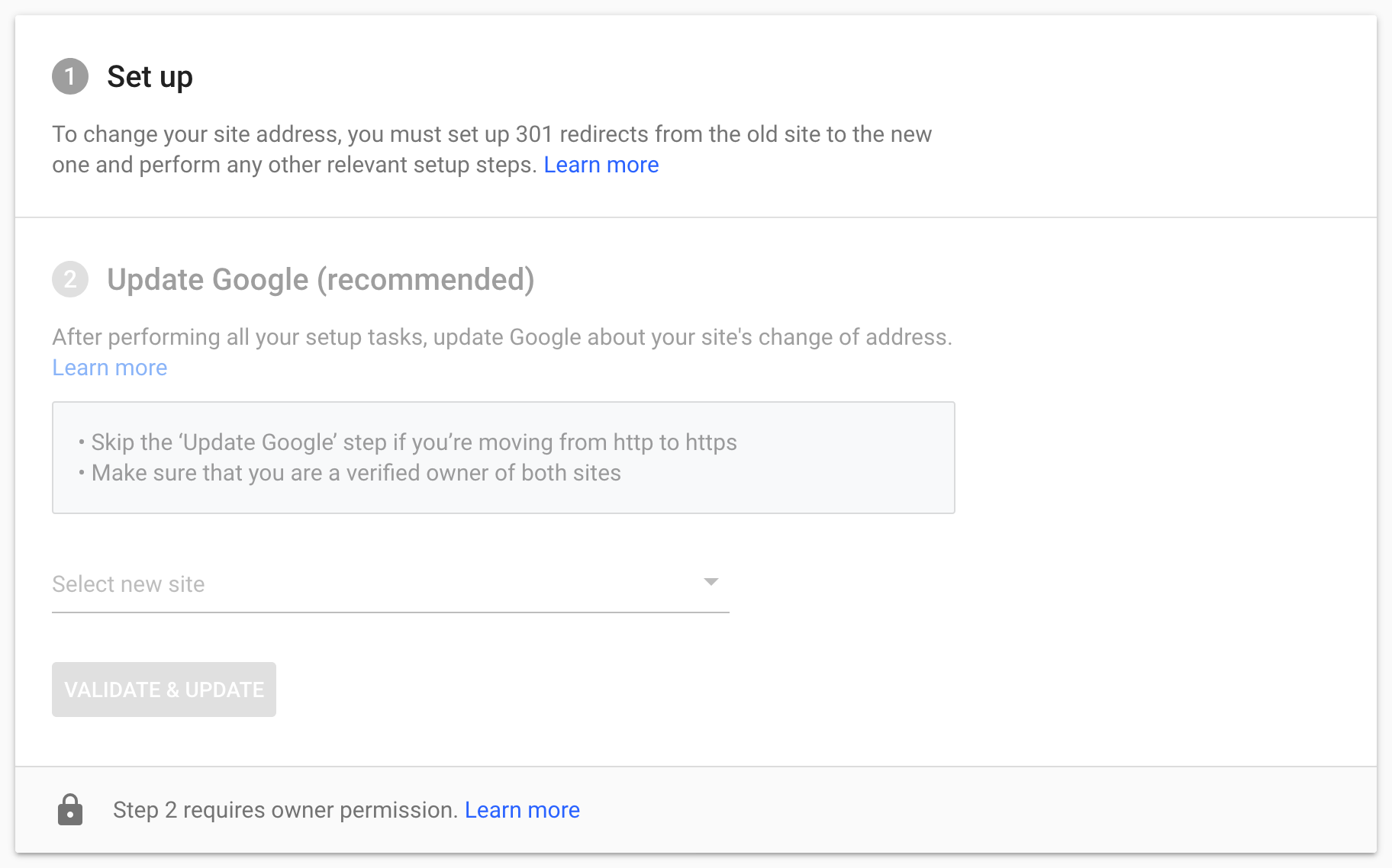
- you have to tell Google about the change of address for the domain, using the GSC
- all content on the old domain has to be redirected to the new domain name, using 301-redirects
- you need to check the internal links
- get Google to crawl the new domain
The change of address tool in the Google Search Console
You can use the Google Search Console to notify Google of a change of address. To do so, you have to add and verify both domains in the same GSC account.
To commit an address change, click on Settings in the left navigation. There you can choose “Change of Address”.
Once the site for the address change has opened, you can select the new domain name from the drop-down list of available properties and sent it to Google.
Now you have successfully requested a change of address with Google.
301-redirects on the old domain
To automatically redirect visitors as well as Google-Bot to the new domain, when they request the old domain name, you have set up a 301-redirect for the old domain name.
In order to use a redirect to the new domain, with a HTTP Status Code 301, you simply enter the following Rewrite Rule into the .htaccess file for the old domain.
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^OLD-domain.com$ [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://www.NEW-domain.com/$1 [R=301,L]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^www.OLD-domain.com$ [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://www.NEW-domain.com/$1 [L,R=301]By using the above code, you will also redirect all URLs. If you, for example, request a URL on the old domain (www.old-domain.com/product-1/), you are automatically redirected to the same URL on the new domain (www.new-domain.com/product-1/).
Checking your internal links
If you used absolute paths for your internal links – which means that whenever you added a link, you used the entire URL as well as the host name – then you should make sure all those links are changed. You would do this by switching the old domain name within every link for the new one.
- you can use the detailed-evaluation of the SISTRIX Optimizer to check your internal link structure
If the internal link structure of your website uses only relative paths then you do not need to change anything.
Have Google crawl the new domain
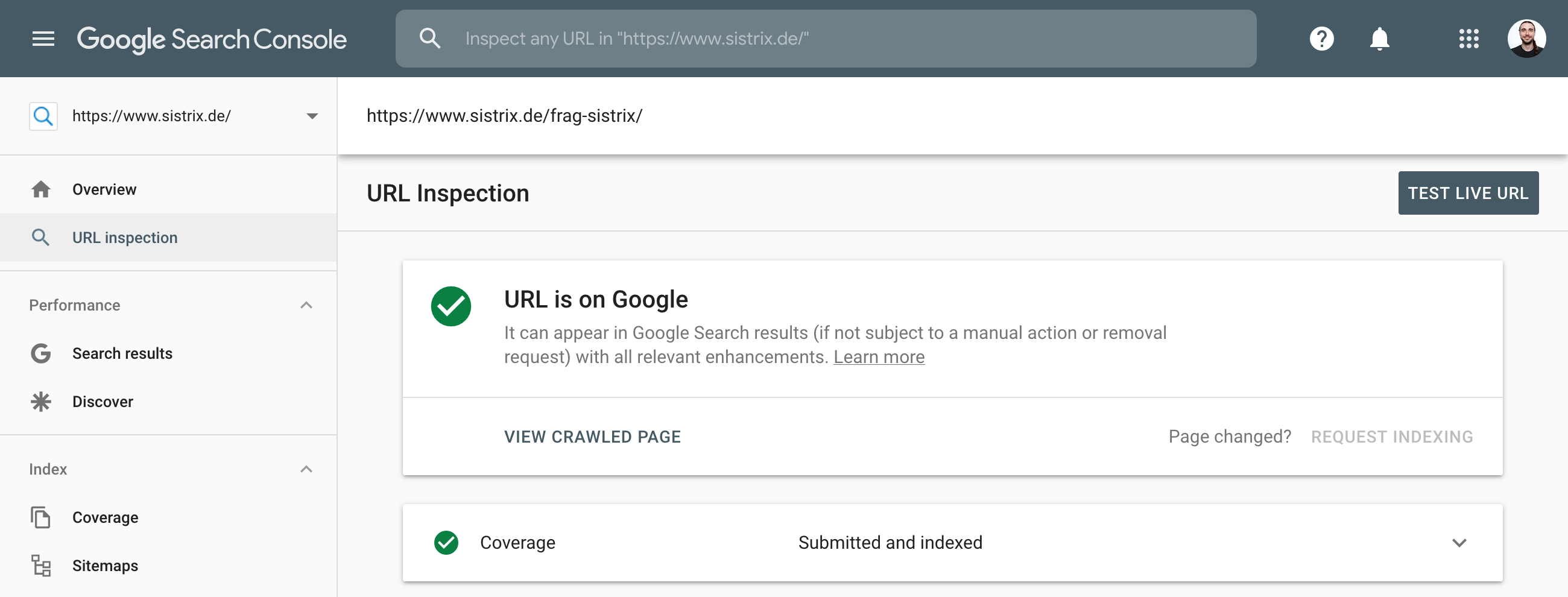
You should request that Google crawl the new website, in order to let them quickly know about the new domain and so that they can index the contents.
To do so, just type the URL you want crawled into the top search bar in Search Console. This will give you access to the “URL Inspection” tool where you can send single URLs to the Google-Index through the “REQUEST INDEXING Indexing” link.
You should also submit a XML-sitemap to Google to support the crawling process.
Monitor your domain move
For the first few weeks, you should regularly check out the crawling-statistic evaluation within the Google Search Console for the new domain – Google recommends 180 days for bigger websites. This way you can quickly identify any crawling problems which may arise.
You can also compare both domains’ Visibility within the SISTRIX Toolbox in order to keep an eye on how successful the domain move has been:
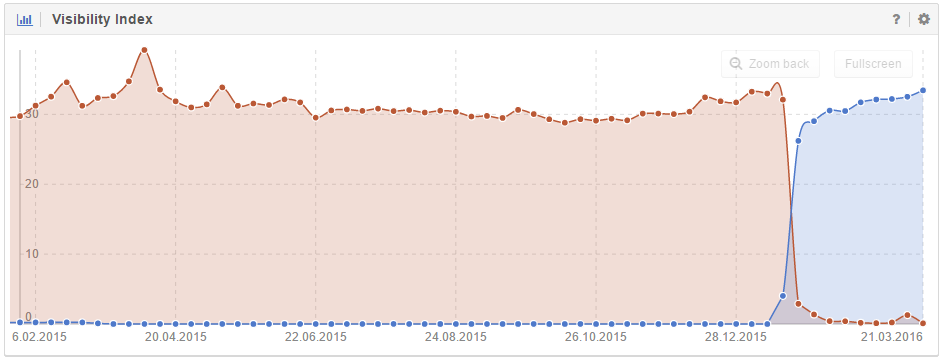
The change in Visibility for both domains clearly shows that, after the move, Google ranks the content on the new domain instead of the old.
301 redirects do not have a high damping factor
A redirect with the HTTP Status Code 301 (Moved Permanently) does not have a higher damping factor than links, says Matt Cutts, Head of Google’s Webspam-Team. According to this, redirecting internal and external links with a 301-redirect is a good choice.
Video: Matt Cutts, Google on multiple 301 redirects
Additional information about this topic:
- Google Help: Moving websites