As there are different types of Google Penalties there is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. Though we can generally differentiate between the two types of penalties.
The algorithmic penalty
A website may have been penalised due to an algorithmic filter, such as a Core Update, Google Panda Update or the Google Penguin Update.
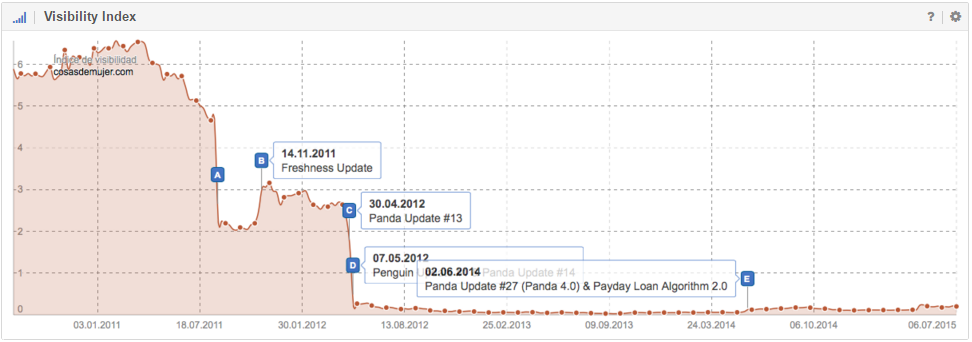
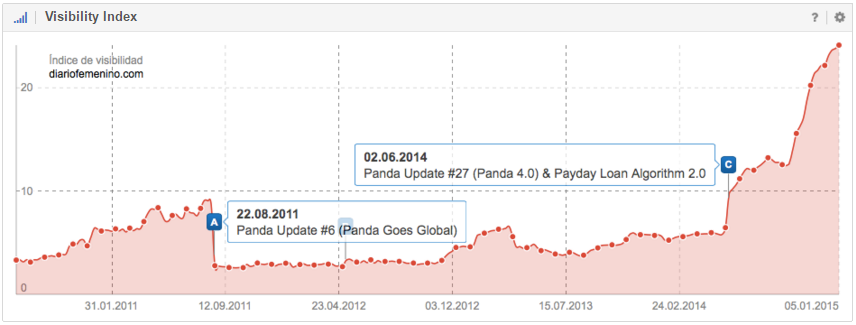
When a website is hit by an algorithmic penalty, both the Visibility and discoverability within the SERPs (Search Engine Result Pages) of the affected domain will take an immediate and serious hit. A continuous and persistent negative trend within the SISTRIX Visibility Index will often come about as a consequence.
You can use the Visibility Index chart of the SISTRIX Toolbox with activated event pins to find out if a domain might have been affected by a filter and thereby inflicted with an algorithmic penalty.
In this case you, as a webmaster, would have to make sure that you change your website in such a way that this or other filters will not find your website to be in violation of the Google Webmaster Guidelines.
With the Core Updates of 2018-2021 Google has been public in saying that there is not much that can be done but data shows that domains are able to recover from previous updates. One must, however, consider that certain searches may have changed intent and that, quite simply, the content that you had ranking, doesn’t fit any more.
Once you have made your website compliant with the Google Webmaster Guidelines the chances of escaping the algorithmic penalty are increased
This domain punished by the Panda Filter had to work on cleaning up for two years before they were able to escape the algorithmic penalty. During this time, Google launched multiple data refreshes for the filter, but the penalty was not lifted automatically until the 26th iteration.
The manual penalty
When a website is manually reviewed by a Google employee, for example because they suspect ranking manipulation due to backlink purchases, a manual penalty can be handed out.
Depending of the extent and the severity of the transgression, a specific time frame will be set for the penalty, during which the website will be punished. This may be around 30 days for a slight transgression against the Google Webmaster Guidelines, for example, and a longer time for a more serious offence. After this time is up, the manual penalty will expire on its own.
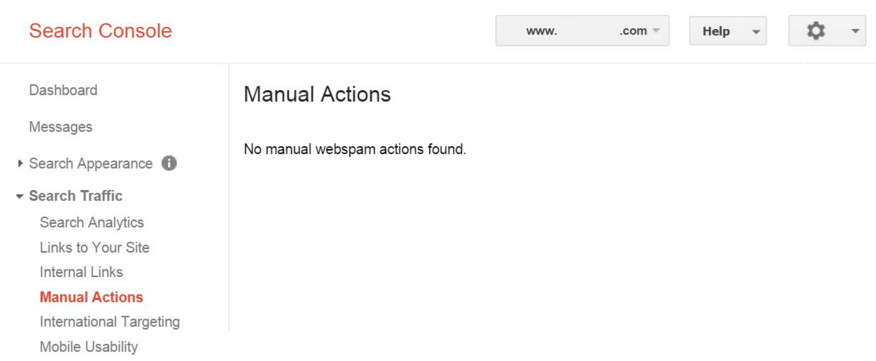
If a website received a manually penalty by Google, there will be a report within the Google Search Console under the “Manual Actions”-menu:
If you receive a notice that a manual action was taken against your site due to “the offence XY” you should start to act and revise your website in accordance with the Google Webmaster Guidelines. Once you have carefully revised the source(s) of the manual penalty you can submit a so-called Reconsideration Request to Google. With the reconsideration request you ask Google to have one of their employees take another close look at your website. If the request is approved and the result of the review is positive, a manual penalty can be lifted early.
Video explanation by Matt Cutts on Google penalties
Additional information on the subject:
SISTRIX