One of the best tools any SEO has on hand is the Google Search Console, or GSC, formerly known as Webmaster Tools. In it, you basically have a control panel of your websites performance in search. Whether you’re an SEO or a website owner, you should connect your domain to the Google Search Console from the start in order to benefit from the useful data within it.
- Lily Ray on Google Search Console. What is it?
- What Is Google Search Console?
- What data can I find in the Search Console?
- Performance
- Coverage
- Experience
- Additional information in GSC
- How to get started with Google Search Console
- Domain Verification
- URL Verification
- What Is The Difference Between Google Search Console And Google Analytics?
- What Can I Do With Google Search Console?
- General Website Stats
- Index
- Enhancements
- Security And Manual Actions
- Legacy Tools And Reports
- Links
- Where is the Crawl stats report in GSC?
- Do I Have To Use Google Search Console To Rank Better In Google?
- Is Google Search Console data the only data needed for SEO?
Lily Ray on Google Search Console. What is it?
What Is Google Search Console?
The Google Search Console is your website’s control panel for Google Search. You can see how many people are visiting your website, what your position in the searches is, how many queries Google found for your website, and if people are actually engaging with your content.
For each page, you can get a detailed report, instructions, and alerts every time something is not working properly. If you have unclickable elements from mobile devices, if you are blocking certain pages from the robots.txt, or if you haven’t submitted a sitemap.
Google Search Console was previously known as Webmaster Tools.
What data can I find in the Search Console?
Here are the main features of Google Search Console as of mid 2021. More details, and information about limitations, are listed below.
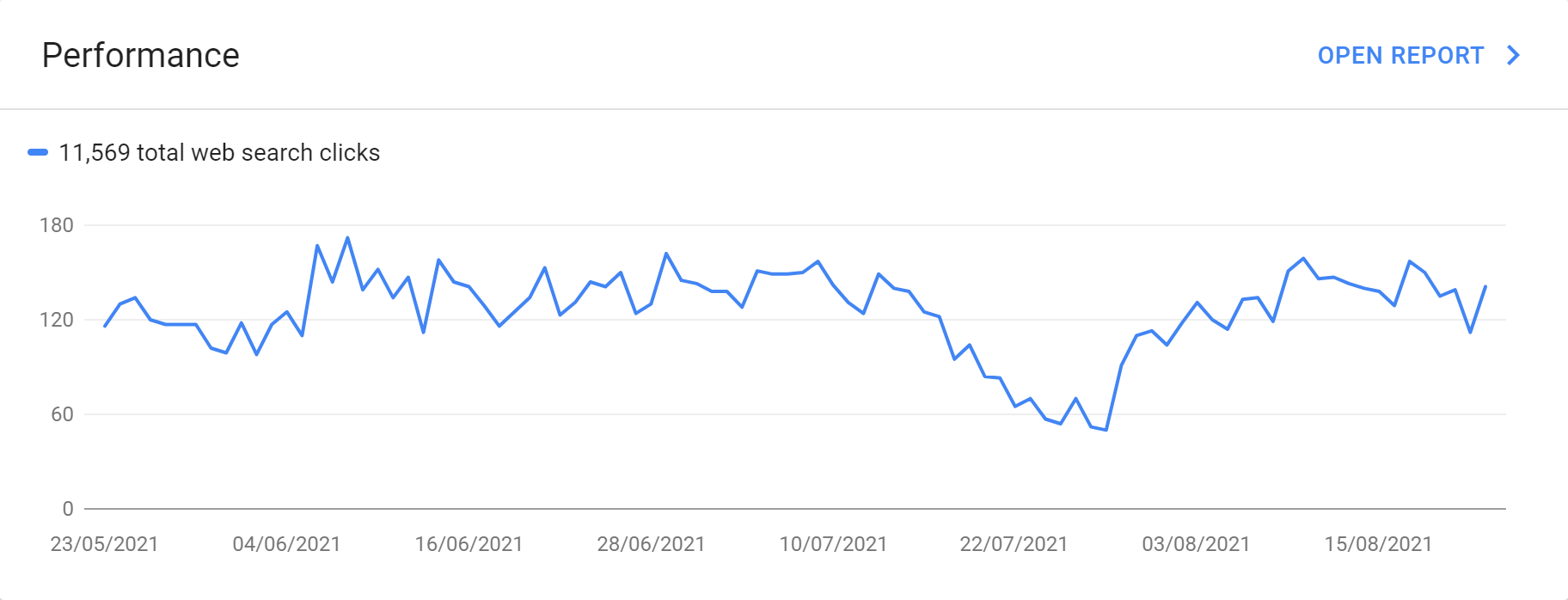
Performance
GSC performance data shows how often the property (domain, host or path) got an impression, the total clicks over the period chosen, average CTR over the period and the average position. By default, the data shown is for all countries and both mobile and desktop data combined. Filters must be used to view individual country and device data.
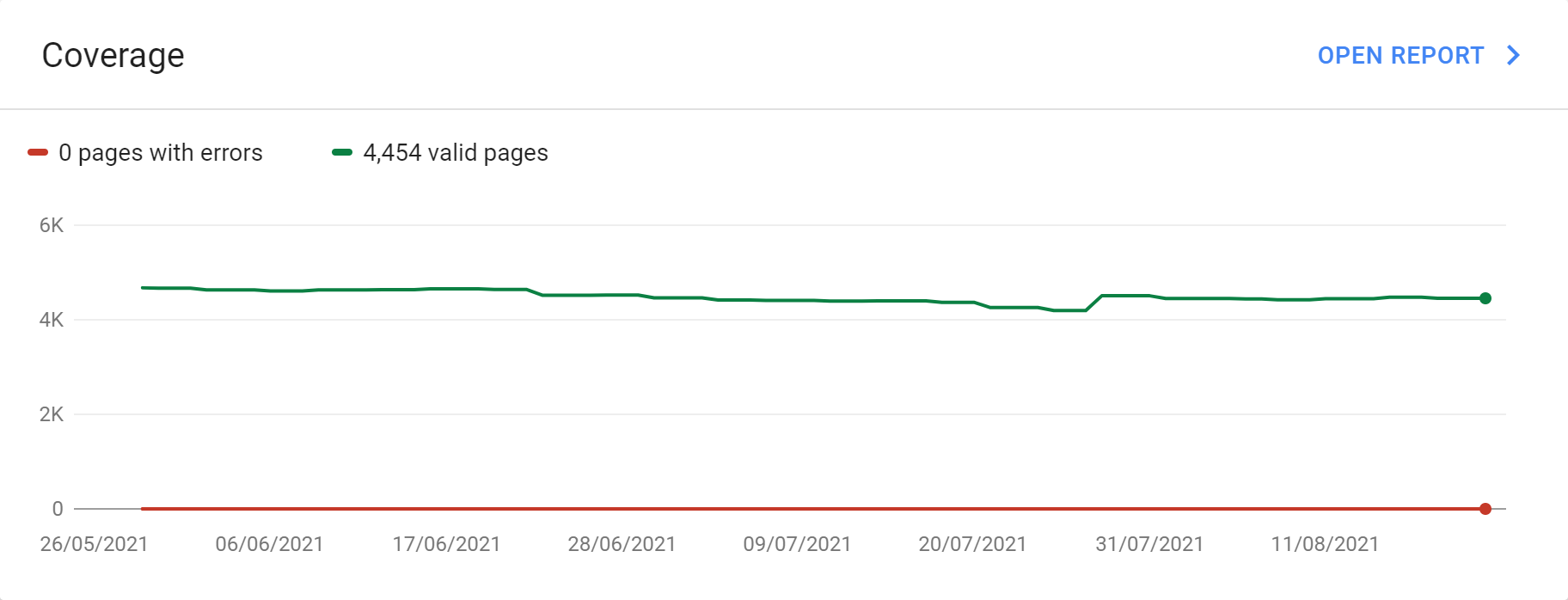
Coverage
The Coverage report includes information on what was crawled and whether it was submitted (a ‘valid page’) in to the Google search index. Pages that are blocked by robots.txt, redirected, excluded by ‘noindex’ tag, soft 404s, canonical issues, page not found issues and duplicate content will be found under the ‘Excluded’ section.
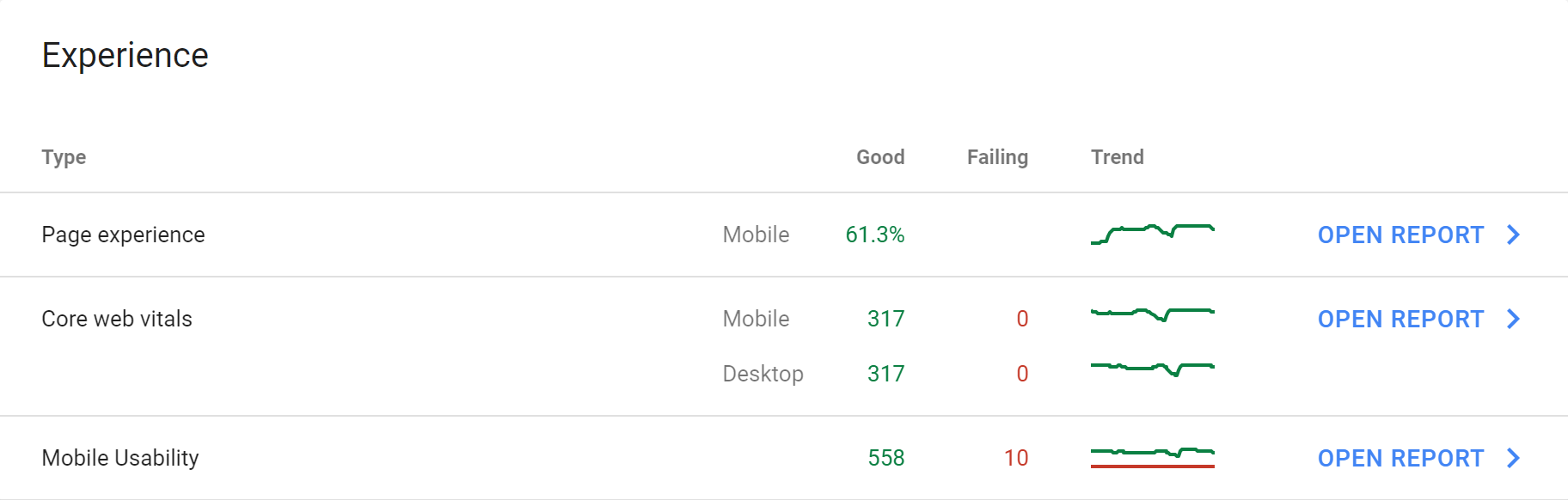
Experience
This section shows quality information such as the Page Experience overview which includes Core web vitals (including page speed and usability factors), mobile view information and HTTPS information.
Additional information in GSC
Apart from the three main sets of data shown above, it’s also possible to see when the report was last updated, what crawler is being used (desktop or smartphone), a detailed crawl stats report, a list of submitted sitemaps, urgent URL removals, security issues, manual actions and links.
Enhanced for 2022 are video and https information.
The Video Pages report shows details about which videos are indexed and which URLs may have issues with video. This is useful for taking advantage of the video elements and features in Google Search Retsults.
The HTTPS report shows pages that aren’t indexed as https pages. This is important as HTTPS is a signal as part of the page experience assessments from Google. More information from Google available here.
There are also some legacy tools still available in GSC, such as international targeting and URL parameters, but these may not be available for domain properties, and may be removed or updated at any time.
More detail on these data sets can be found below, but first, the important task of setting up a domain in Google Search Console.
How to get started with Google Search Console
The first thing you need to do in order to access the Google Search Console for your website is to connect your domain. You have a few different methods of verifying your ownership. Needless to say, you won’t be able to see a website’s stats if you are not the owner or expert in charge, so you need to start by adding your property.
Here’s the starting page for the Google Search Console. Make sure you use this with a Google registered email address.
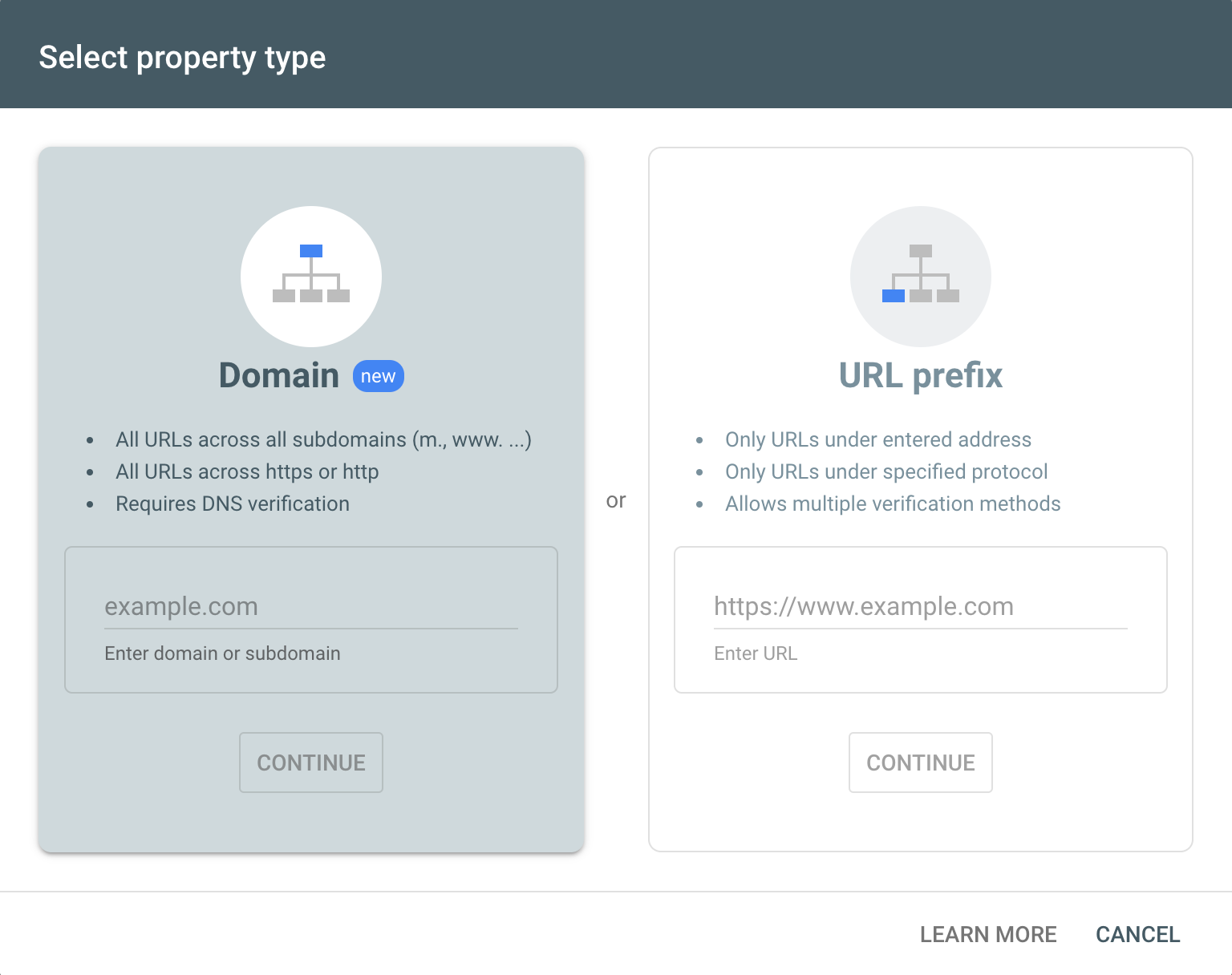
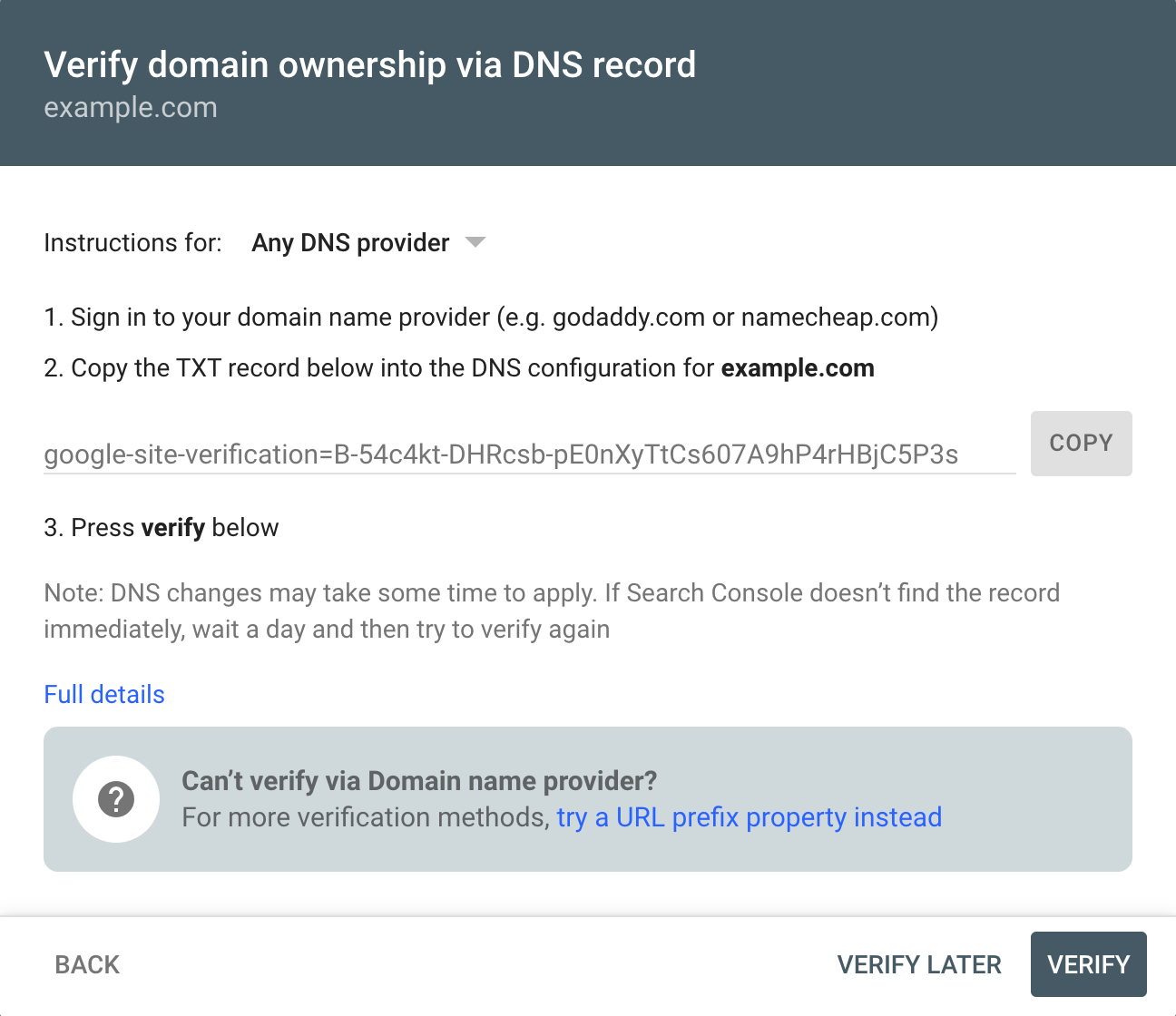
Here, you have two options. You can either use the domain name or a URL. The main difference between them is that the URL allows you to choose specific addresses to measure (hosts or subdirectories for example). The domain verification gives involves editing the DNS records in your hosting, while the URL verification allows you to enter a key generated by the Google Search Console in your website’s code.
Domain Verification
For the domain verification, you will need to edit your DNS records from your hosting service. The GSC will generate a code which you can use to add a new “text” type record, and then wait for it to be confirmed. This is the option Google recommends in order to have full access to the GSC, and your host providers can help and change the record for you.
URL Verification
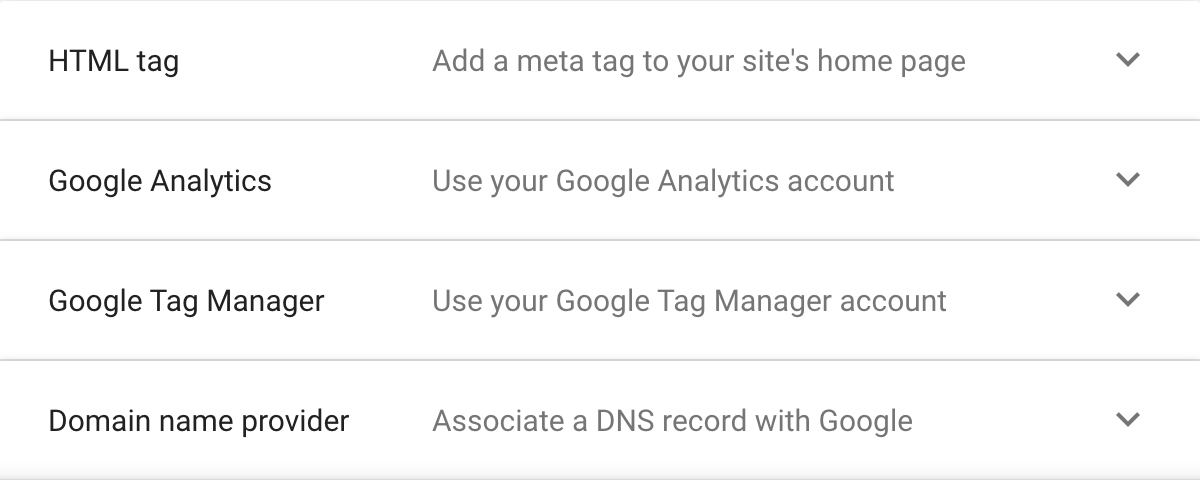
For the URL verification, you have four options to choose from. You can either add a key into your website’s code, use Google Analytics if you have it set up, use Google Tag Manager, or associate a DNS record. Some platforms, such as Shopify, give you the option of adding the code in your settings, thus making the process faster.
A very important thing that it’s worth mentioning here is the fact that if you submit a domain to the GSC, you will start tracking all the URLs it contains. If you only want to track a certain part of the domain, then use the URL verification for a specific address.
What Is The Difference Between Google Search Console And Google Analytics?
Both Google Search Console and Google Analytics have their own purpose. While the GSC is meant to help the owners and webmaster see and solve all the matters related to the search engine, Google Analytics offers you insights from a marketing perspective, about how the users interact with your website, conversion rates, and data about your audience.
There is no way of saying which one of these is better, as they fulfil different purposes. You need Google Search Console to identify the technical problems, and you need Google Analytics in order to identify your target audience, and create specific content in order to engage with it,
What Can I Do With Google Search Console?
Let’s take each of the Google Search Console functions, and see exactly what you can do with it, in order to improve your website’s rankings. Before we get into that though, it’s worth considering some of the limitations of Google Search Console data.
General Website Stats
In the first tab, you can see the Overview, Performance, and URL Inspection screen.
Overview
In the Overview, you can see your website’s performance in the SERPs. It shows you how many clicks you get, how many pages you have along with their quality and enhancement. This is where you begin, and most times, the first stats you encounter.
Performance
In the performance tab, you will see all a detailed view of your stats. Everything is divided into four tabs: total clicks, total impressions, average CTR, and average position.
The total clicks number is pretty straightforward. It gives you the number of clicks your website’s search results received in a specific timeframe.
The next one is the number of impressions. This one shows you how many times your website showed up in the searches, and was viewed by possible visitors. This is a very important number, and if you look closely at the number of clicks and impressions, you can determine what your conversion rates are, and see what you can improve.
The CTR is the click-through rate, meaning how many people saw your link and clicked on it. Any webmaster aims to have high conversion rates, but if that doesn’t happen, you can check out every link and see how you can improve them.
Lastly, you have your website’s average position in the SERPs. The number is calculated based on all your pages, and it’s important to also check each page separately. While some pages may rank first, others may be on the second or third pages, so it’s something you need to look into.
Under each graphic, you can check out your queries, pages along with their stats, demographics, devices, search appearance, and the dates your content was updated.
URL Inspection
The URL inspection tool allows you to manually check every URL for indexing, coverage, and enhancements. Front this tab you can manually submit URLs for indexing, if you need to.
Index
The index tab holds some of the most important data, such as coverage, sitemaps, and removals.
Coverage
The coverage tab is where you can see the technical data about all your links. It’s very important to keep an eye on this data because you get to see all the pages you excluded from the index, and all the pages that are out there and valid.
Since you will be blocking some of the pages, especially in the case of online stores where you need to block filters, checkout pages, and wish lists, you can check them out in the GSC and get an overview of the situation.
Sitemaps
XML sitemaps are formatted lists of your websites pages, that tell the search engines what they are and where they are to be found. A website will be indexed with or without a sitemap, but in some cases a sitemap can help. You can find out more about sitemaps here.
In this tab, you will be able to see what sitemaps you have already submitted, their status, and the date they were last crawled. It’s important to keep an eye on this tab and see if any errors occur.
Removals
The GSC offers us the possibility of removing URLs from the index. This can be absolutely mandatory if you change the structure of the website, relaunch, or simply want to remove outdated content. You can simply submit a request, and Google will take care of the rest. It’s not always necessary to manually remove a URL through GSC. See option #1 for another way to remove URLs.
Enhancements
The enhancements are signals Google uses in order to determine the overall user experience. It’s very important for any website to have a fast loading speed, a secure connection, and to be optimised for mobile devices.
Core Web Vitals
The core web vitals are some of the most important aspects of the GSC. Based on these metrics, the search engine will (planned for 2021) decide on whether your page is optimised or not and offering its visitors a good user experience. Right now, in the core web vitals, we’re talking about loading speed, interactivity and visual stability. Because Google’s purpose is to help people get the information they need, the core web vitals will soon be a ranking factor.
Mobile Usability
The Mobile Usability report gives you the information you need about how your mobile visitors are interacting with your website. For each page, you can either get an “Error” or “Valid” status. Of course, an “Error” status involves you checking the issue, and fixing it as soon as possible. Google also offers a mobile-friendly test tool if you want to check each page separately, and then you can process to following that page in your GSC, as long as you are the domain owner.
Security And Manual Actions
Because the security of a website is highly important, you will be able to see all the problems affecting you directly in your Google Search Console. While manual actions are considered to be penalties, in the security tab you can see possible breaches on your domain.
Manual Actions
Manual actions, as mentioned, can also be considered manual penalties. Where they are given, you will need to fix them as soon as possible. Google has the mission of keeping the internet safe and useful for everyone, so if it discovers that a website has duplicate content, pages with irrelevant content, too many keywords, malware or even abusive structured data, it may issue a manual penalty towards that page or website.
We’ve written more detailed documentation on manual penalties here.
Security
In the Security tab of your Google Search Console, you can see if and how your website is affected by malware, hacking, or social engineering. In general, here we are talking about issues affecting the website from the outside, and it’s important to take a look at the security issues report, guidelines, and the actions you may be required to take.
Legacy Tools And Reports
The Legacy Tools are the ones that aren’t yet implemented in the new Google Search Console. You can find information about crawling, and how often GoogleBot is doing it, URL parameters, international targeting, and access various tools that can help you keep track of your domain’s activity in Google search.
Links
The Links tab helps you keep an eye on all your internal and external links. This is an important management tool, and it can help you see what other sites are directly referring to your domain. You can apply filters in order to only find specific linking domains, and also see the anchors people used to link back to you.
Where is the Crawl stats report in GSC?
Yes, it’s hidden! Go to Settings, in the left-hand menu system, and you’ll see “Crawling” listed. Click on OPEN REPORT. If you’re logged in, click here and if you’ve go multiple properties (domains, hosts, paths) connected to GSC it will ask you to select one (on the top-left drop-down menu.)
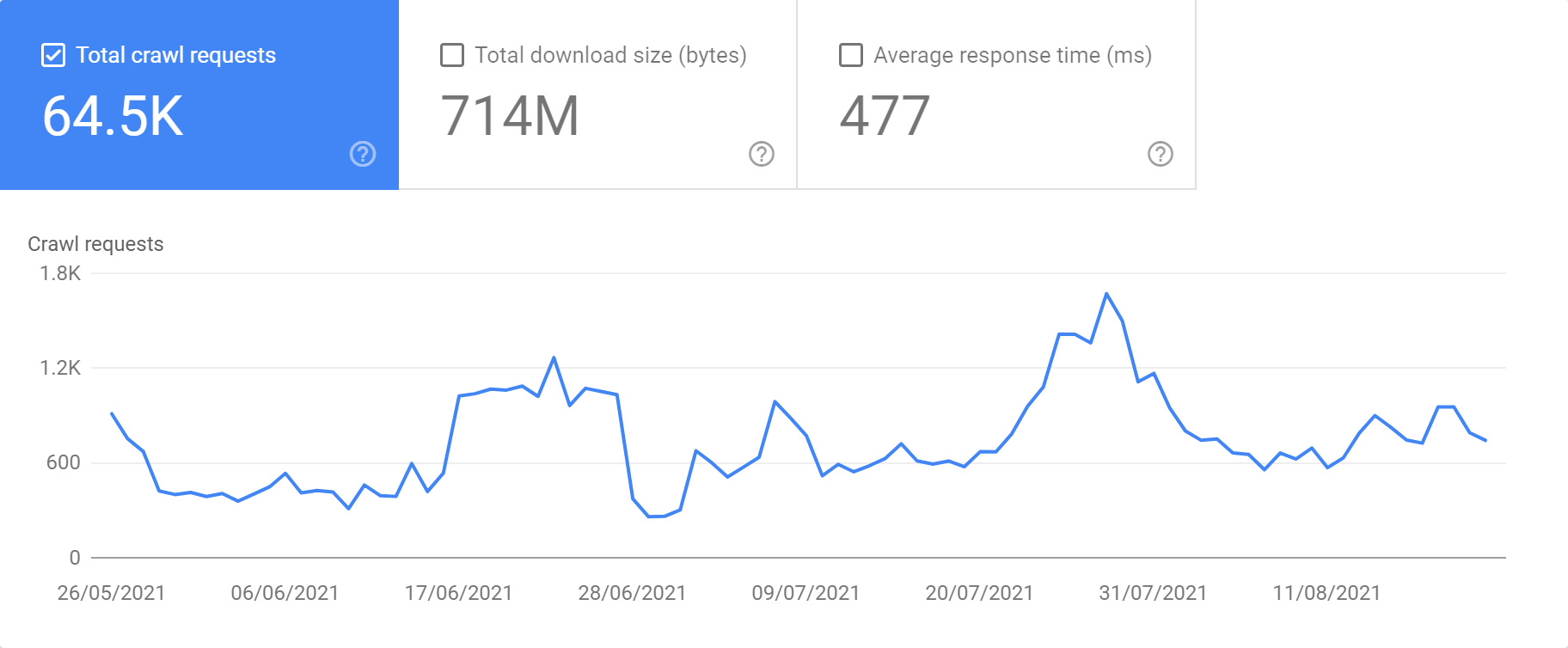
The Crawl stats report will give you information on Total crawl requests, Total download size and Average response time. Further into the report you’ll find data on response codes, file types, purpose (Refresh or Discovery) and Googlebot type.
Do I Have To Use Google Search Console To Rank Better In Google?
No tool will assure your rankings, but using the Google Search Console gives you a very good view on where your website stands in the SERPs, and how Google is discovering it.
Google Search Console gives you the following advantages
- Free to use
- Data is from Google
- Wide range of functions
- Give a good overview of crawling and indexing
- Shows crawling issues.
- Give information on mobile crawling, page speed and usability
- Helps with information on how to improve
- Allows content to be removed from the Index
- Allows content to be tested and submitted
- Offers further functionality through an API
Ranking a website is a continuous effort, and you need to use all the tools you have at your disposal in order to get it to the first page. The good part is that Google offers its users usable tools in order to get to that point.
Is Google Search Console data the only data needed for SEO?
In short, no. GSC data has limitations and the reports, especially the click reports, can be influenced by factors outside SEO. For example, there may be increased clicks to Formula 1 racing traffic, in-season and on race weekends. Weather, global events and news can also heavily affect click numbers.
Here’s a summary of things to be aware of when dealing with Google Search Console Data.
Google Search Console doesn’t show any information about competitors and is, therefore, a bad benchmark. You clicks may be rising, but your competitor clicks might be rising faster.
If a page is not seen in the search results, it’s not collected by GSC. This can lead to some niche or out of season keywords not appearing.
Ranking distribution, a strong measure of content success, cannot be determined through GSC data as results on page 2-10 may never be access by users and won’t trigger results in the GSC report.
Average positions can be confusing. Decimal places are included and URLs appearing twice can lead to averages that hide the appearance of higher positions.
Delayed data. It takes Google a few days to get the final data into the reports.
More information on these points are available in a SISTRIX article: Google Search Console: Differences and Limits