When confronted with a search request, Google attempts to classify the user’s intent. Does the user want to do something, learn something, visit a website or visit a physical location? The intent can often affect the layout and features in its results and, in turn, this affects the clickthrough rates.
This article summarises the results of our extensive analysis of search features and provides you with a quick overview of the important CTR figures for each of the common search result feautres..
- Summary: Click through rates for different search result features
- How SERP Layouts Affect CTRs
- CTR Benchmarks: What’s a “Good” CTR?
- Factors Affecting SERP Layouts
- Search Features - What do they look like?
- Purely Organic SERP
- Sitelinks
- Featured Snippets
- Google Apps
- Knowledge Panels
- Shopping
- Google Ads
- Chart: CTRs for various search features.
- The Effect of Intent on SERPs and CTRs: A Final Word
Discover how SISTRIX can be used to improve your search marketing. 14 day free, no-commitment trial with all data and tools: Test SISTRIX for free
Summary: Click through rates for different search result features
For those of you that need the answers right up-front, take a look at this table which shows the SERP features and their effect on the first, second and third CTRs. These results are for the important mobile SERPs.
| SERP Feature | CTR Position 1 | CTR Position 2 | CTR Position 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purely Organic | 34.2 | 17.1 | 11.4 |
| Sitelinks | 46.9 | 14.0 | 5.6 |
| Featured Snippets | 23.3 | 20.5 | 13.3 |
| Google Apps | 16.3 | 16.7 | 13.2 |
| Knowledge Panels | 16.8 | 13.2 | 12.6 |
| Shopping | 13.7 | 8.0 | 6.4 |
| Google Ads | 18.9 | 8.8 | 6.3 |
| Videos | 32.5 | 16.0 | 10.6 |
| Images | 18.5 | 12.6 | 9.1 |
| Local | 17.7 | 14.2 | 9.1 |
| News | 21.0 | 14.2 | 9.9 |
| Recipes | 25.5 | 16.8 | 12.0 |
| AVERAGE | 28.5 | 15.7 | 11.0 |
For information on how this data was collected including more summary findings, details on our methodology, read our original CTR report, or carry on here for more information on the SERP layout, why it affects CTR and the types of features that we analysed in the study.
How SERP Layouts Affect CTRs
Dozens of features (we’re currently tracking 45 different types of search feature) can appear on the SERP that often reduce clickthrough rates (CTRs) for organic search results by providing information right on the SERP page.
These feature-rich integrations can include images, product listings, Q&As and other elements that can often distract or divert a user from their original query as they scroll through the results.
Remember the old days when you would google a currency exchange rate and had to visit a website? Now you see it right on top of all the other search results.
That’s just one example of an integration that lowers CTRs.
And to put it plainly, more features = a lower CTR.
CTR Benchmarks: What’s a “Good” CTR?
Often we’re asked about what a “good” CTR is. The question may be short but the answer is far more complicated.
After a comprehensive detailed analysis of over 80 million keywords and billions of search results, the best answer we can give is “it depends”.
The truth is that average CTRs actually distort reality because they are, well, “average”.
Generally speaking, the average CTR for the first position in Google is 28.5% followed by 15.7% for the second position and 11% for the third position. But that’s about as meaningful as lining up 100 people of all ages and stages, asking them to run 100 meters, dividing the total result by 100, and stating that the “average” is reality.
It’s not, of course. Like the natural world, the internet is a very diverse place.
Factors Affecting SERP Layouts
CTRs vary across industries and keyword environments and are increasingly becoming dependent on SERP layouts. With that in mind, it’s necessary to evaluate CTRs in the context of different SERP integrations and how Google search intent affects the results pages.
For example, a search for a very popular term like “keto diet” will show a feature-rich results page that includes advertisements, frequent questions, and book suggestions.
Accordingly, a long-tail search such as “will the keto diet help with diabetes” shows advertisements, books, plans and other items that can be purchased. Following all these features, organic searches are then displayed which, in some cases, have a lower likelihood of clicks.
Conversely, a search like “keto diet scientific studies” will produce a list of purely organic search results.
Google clearly classified different intents behind all these searches and outputted differing SERP layouts in response.
Search Features – What do they look like?
The table above (and repeated below) lists average CTRs in context of the additional integrations found on SERP pages. Here is a list of the common SERP features used in our analysis
Purely Organic SERP
A purely organic layout is a list of results in plain blue clickable links without any distracting elements, like the early days of the internet.
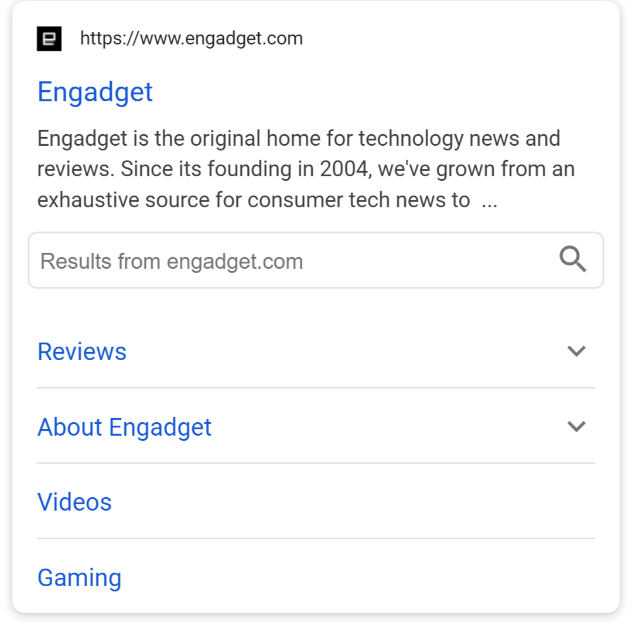
Sitelinks
Sitelinks are shown in the SERPs if the Google algorithm believes that there is a clear intent to find a website. This is often true in cases where someone does not know the exact URL or is new to the internet and does not understand how a web browser works.
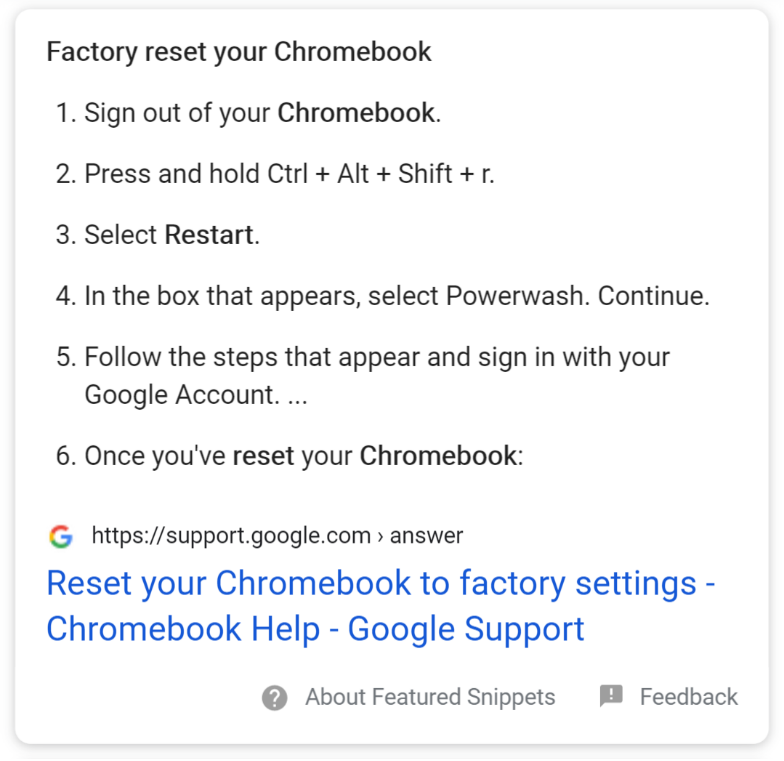
Featured Snippets
Featured Snippets are highlighted organic results that Google provides when it believes the user has a “know” intention. Besides text, images and tables are also displayed to provide answers directly on the SERP page.
Google Apps
Google Apps is a more feature-rich version of a Featured Snippet that provides the user with information in the case of a “know” intention.
This integration is often seen in searches asking for the time in a specific country, currency conversion or temperature conversion. These answers are usually displayed on top of the search results.
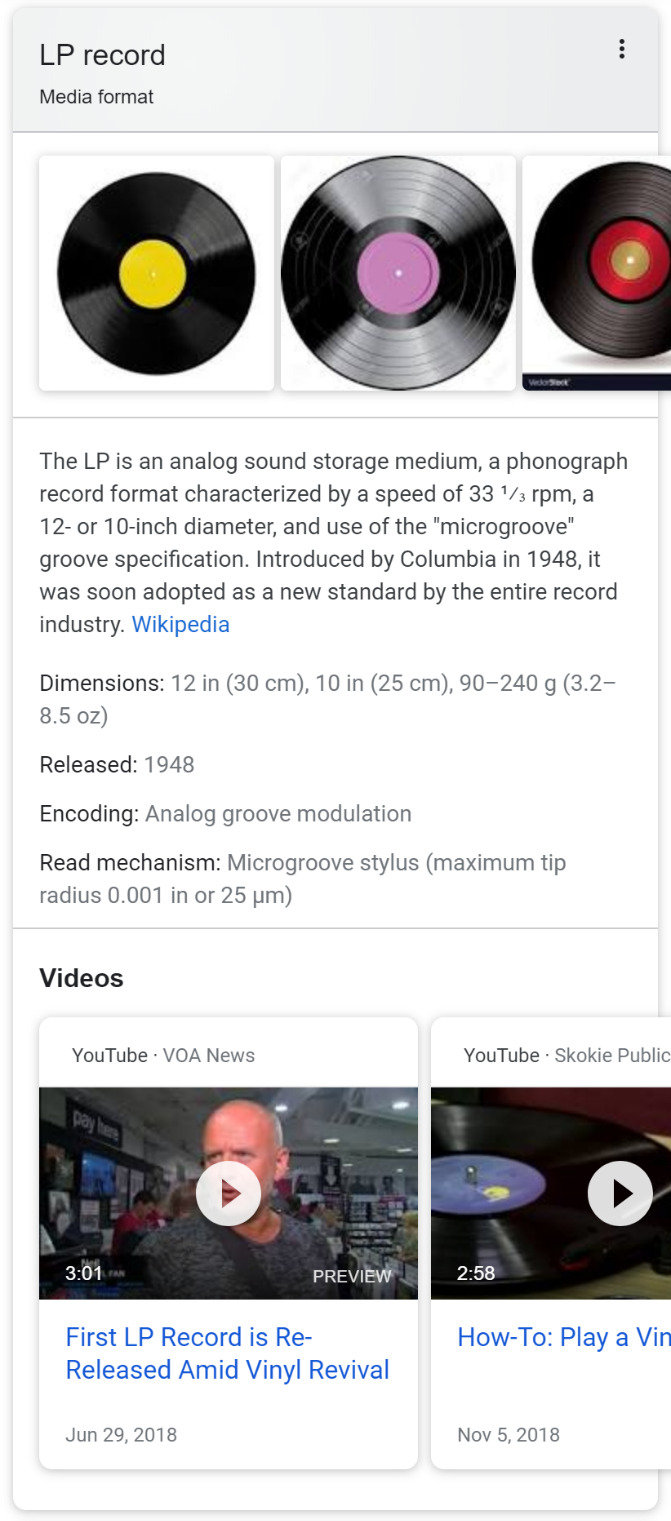
Knowledge Panels
Knowledge panels are information provided by Google that list details on the item being searched. Located on the right next to the results, this information is provided when Google believes there is a “know” intention.
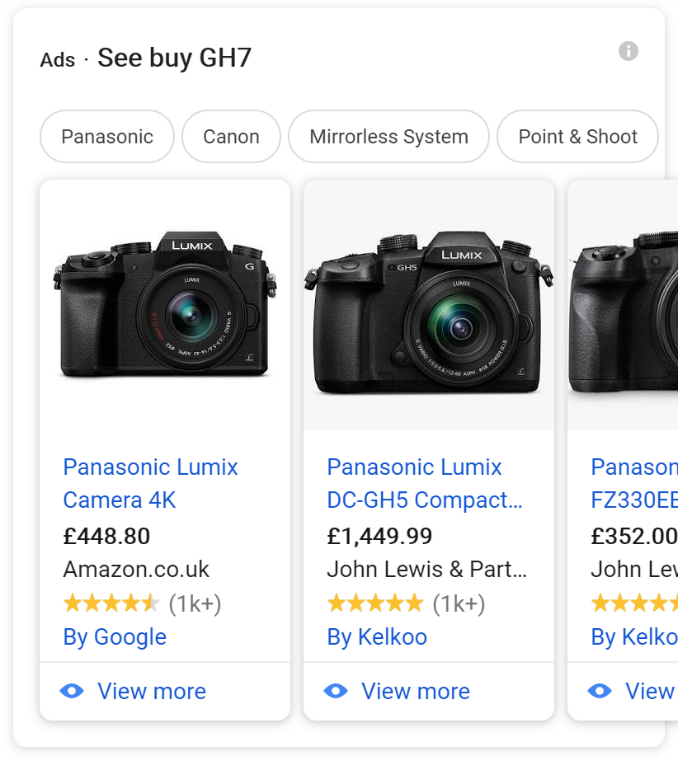
Shopping
The Shopping feature displays e-commerce advertisements provided by Google. Found at the top of the SERP, it accounts for the lowest CTR at 13.7% for the first result with below-average click rates for all other results.
Google Ads
Google Ads are advertisements that use a bidding process to optimize the order of the advertisements being displayed. Found at the top of the SERP, Google Ads are often not distinguishable from organic listings by most users.
Videos
Video boxes are another feature that has been integrated into the SERPs that provide users with video content based on their inputted keywords.
Images, Locations (Local), News, Recipes
These are other features provided by Google that are increasingly being integrated into the SERPs that provide information directly on the results page.
Chart: CTRs for various search features.
Once again, here’s the summary chart.
| SERP Feature | CTR Position 1 | CTR Position 2 | CTR Position 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purely Organic | 34.2 | 17.1 | 11.4 |
| Sitelinks | 46.9 | 14.0 | 5.6 |
| Featured Snippets | 23.3 | 20.5 | 13.3 |
| Google Apps | 16.3 | 16.7 | 13.2 |
| Knowledge Panels | 16.8 | 13.2 | 12.6 |
| Shopping | 13.7 | 8.0 | 6.4 |
| Google Ads | 18.9 | 8.8 | 6.3 |
| Videos | 32.5 | 16.0 | 10.6 |
| Images | 18.5 | 12.6 | 9.1 |
| Local | 17.7 | 14.2 | 9.1 |
| News | 21.0 | 14.2 | 9.9 |
| Recipes | 25.5 | 16.8 | 12.0 |
| AVERAGE | 28.5 | 15.7 | 11.0 |
The Effect of Intent on SERPs and CTRs: A Final Word
In the past, search volume was used as a primary metric for evaluating the potential of a keyword. Those days are now over.
Google’s new SERP layouts – based on the user intent “do”, “learn”, “visit” (website) and “visit” (place) should now be factored into our methodology for evaluating the potential for clicks.
The importance of user intention will only increase as Google’s algorithm continues to mature, prompting for more “On-SERP-SEO” techniques aimed at optimizing these integrations.
Test SISTRIX for Free
- Free 14-day test account
- Non-binding. No termination necessary
- Personalised on-boarding with experts